
|
Developed by 

|
Supported by 

|
Bictegravir (BIC)
Developer(s)

|
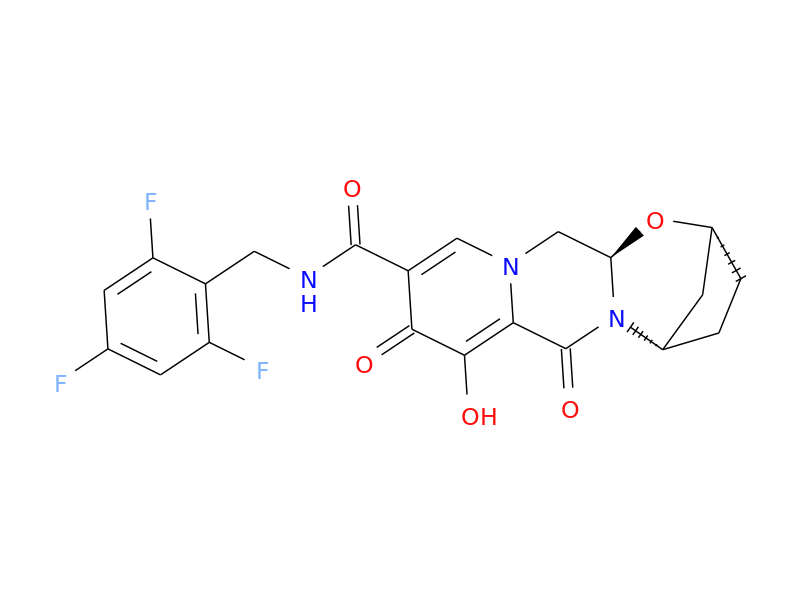
Drug structure

Bictegravir chemical structure
MedChemExpress
Drug information
Associated long-acting platforms
Oral solid form
Administration route
Oral
Therapeutic area(s)
Use case(s)
Use of drug
Ease of administration
Frequency of administration
User acceptance
Not provided
Dosage
Available dose and strength
various fixed dose combinations
Maximum dose
Not provided
Recommended dosing regimen
Not provided
Additional comments
Not provided
Drug information
Drug's link(s)
Not provided
Generic name
Brand name
Compound type
Summary
Approval status
Regulatory authorities
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Scale-up prospects
Not provided
Tentative equipment list for manufacturing
Not provided
Manufacturing
Not provided
Specific analytical instrument required for characterization of formulation
Not provided
Clinical trials
Not providedExcipients
Proprietary excipients used
No proprietary excipient used
Novel excipients or existing excipients at a concentration above Inactive Ingredients Database (IID) for the specified route of administration
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
Residual solvents used
No residual solvent used
Patent info
There are either no relevant patents or these were not yet submitted to LAPaL
Supporting material
Publications
There are no publication
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
There are no additional links
Access principles
|
|
Collaborate for developmentConsider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology Not provided |
|
|
Share technical information for match-making assessmentProvide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit Not provided |
|
|
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICsIn the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing Not provided |
Comment & Information
Not provided