
|
Developed by 

|
Supported by 

|
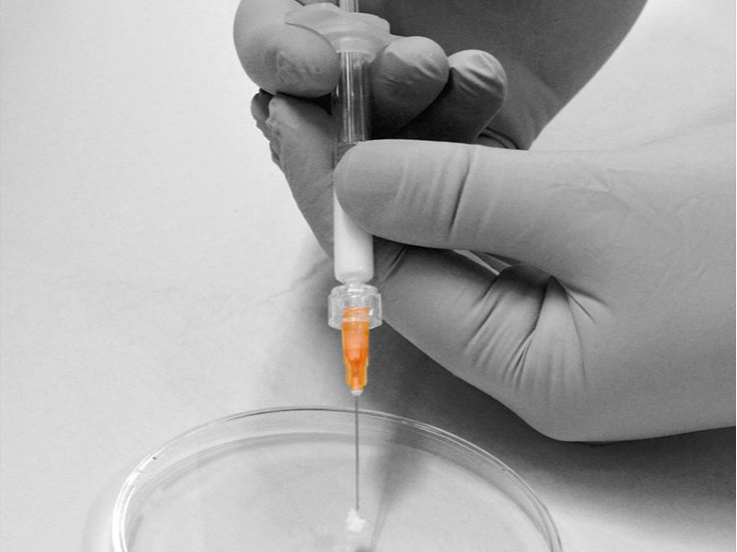
DelSiTech Silica Matrix Drug Delivery
Verified by the innovator, on Mar 2022Developer(s)

|
DelSiTech https://www.delsitech.com/Finland DelSiTech is the world technology leader in advanced biodegradable silica based controlled release materials |
Sponsor(s)
|
|
- - |
Partnerships

|
Innovare r&d http://www.innovare-rd.com.mx/ |

|
Bayer https://www.bayer.com/ |

|
Astrazeneca https://www.astrazeneca.com/ |

|
Visus Therapeutics https://www.visustx.com/ |
|
|
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation https://www.gatesfoundation.org/ |

|
UNITAID https://unitaid.org/#en |
Technology information
Type of technology
Silica microparticles; silica hydrogel; silica microparticles and silica hydrogel composite,, Biodegradable monolithic solid silica implant, Inorganic nanoparticles
Administration route
Subcutaneous, Intra-articular, intratumoral, intraocular, intrathecal and transtympanic, Intra-vitreal, Intramuscular, intratumoral, intraocular, intrathecal and transtympanic
Development state and regulatory approval
Entecavir (ETV)
Pre-clinical
No
Description
Long-acting injectables (parenteral administration) and topical eye drops drug delivery technology where the active substance is embedded and released in controlled manner from a biodegradable silica microparticle-silica hydrogel composite material, with release period tunable from a day to several weeks, months up to a year.
Technology highlight
DelSiTech Silica Matrix long-acting drug delivery technology is adaptable to any therapeutic agents: from small molecules to peptides and complex biologics. The technology is compatible with high API loading, but also with poorly or highly soluble molecules. True controlled release that can be tuned from days up to a year, following zero-order release profile with no or limited burst release. The final dosage form is a ready to use prefilled syringe with 24 to 30G needle. Silica microparticle-silica hydrogel depot can be easily removed as one piece in case of adverse effects. With eyedrops the release can be adjusted from 24 to 48 hours with stable API concentration even overnight with a single drop.
Technology main components
The formulation contains only one main excipient silica (SiO2). in addition, WFI (water for injection), and pH controlling agents (in the hydrogel component).
Information on the raw materials sourcing, availability and anticipated price
Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) the silica precursor is widely available material used for various application.
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
API desired features
Not provided
Additional solubility data
Not provided
Additional stability data
APIs are stable in solid silica microparticles. There is no chemical/biological interaction with the Silica nor with external environment.
API loading: Maximum drug quantity to be loaded
30-50 wt%
API co-administration
2 different APIs : No technical limits.
LogP
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Scale-up prospects
Spray-drying process is highly scalable process and widely used.
Tentative equipment list for manufacturing
Mixer and pumping prior spray drying. Spray drying equipment. Fill and finish equipment
Manufacturing
Normal manufacturing requirements for spray drying and aseptic fill and finish.
Specific analytical instrument required for characterization of formulation
HPLC equipment, capability to perform immunoassays and the appropriate detection equipment required by the API. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) instrument for particle size distribution. Dissolution for release characteristics in water bath in shaking. Silica measurement with microwave plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (MP-AES) or with spectrophotometric measurements. Rheometric analysis (oscillation and rotation), manual injectability and injection force measurement. SEM analysis for visualizing the particles. NMR for measuring silica condensation.
Clinical trials
Not providedExcipients
Proprietary excipients used
No proprietary excipient used
Novel excipients or existing excipients at a concentration above Inactive Ingredients Database (IID) for the specified route of administration
Can be determined with a partner. Can be introduced during clinical studies.
Residual solvents used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
Other features of the technology
- Biodegradable
- Single-use
- Room temperature storage
- Monolithic
- Removable
- Other(s)
+4 to +8 degrees Celsius storage may be needed in some cases
Release properties
Release time is adjustable: as fast as one day or as slow as one year. The release is based on surface erosion mechanic.
Injectability
Silica microparticles-hydrogel depot has shear thinning properties and can be used with pain-free needles up to 30G.
Safety
Silica is inert, non-toxic and completely bio-dissolvable. The main degradation product is soluble silicic acid that is a natural component of the body. Silica is accepted for topical use and tox tolerability data available for injectables.
Stability
The APIs is homogeneously dispersed and encapsulated in inert solid silica microparticles, maintaining high chemical stability and biological activity for the APIs
Storage conditions and cold-chain related features
Room-temperature storage if encapsulated drug does not require refrigeration
Potential application(s)
Therapeutic area(s)
Use case(s)
Use of technology
Ease of administration
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
- To be determined
- Self-administered
Frequency of administration
Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Every 6 months, Yearly, Every 2 months
User acceptance
Not provided
Targeted user groups
Age Cohort- Adults
- All
- Male
- Female
- Cisgender female
- Cisgender male
- Transgender female
- Transgender male
- Intersex
- Gender non-binary
Pregnant individuals
Yes
Lactating individuals
Yes
Healthy individuals
Yes
Comment
Those who would benefit from longer dosing intervals or for whom adherence to current treatment might be challenging.
Potential associated API(s)
Entecavir (ETV)
Class(es)
antiviral
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Hepatitis B treatment
Foreseen user group
People living with hepatitis B chronic infection
Foreseen duration between application(s)
2 months
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
No
Immunoglobulins
Class(es)
Monoclonal antibody
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
-
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
HIV PrEP
Foreseen user group
Individuals at risk of contracting HIV
Foreseen duration between application(s)
To be determined
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
-
Antivirals for systemic use, Cabotegravir (CAB), Dolutegravir (DTG), Islatravir (ISL)
Class(es)
Dolutegravir, cabotegravir, islatravir etc.
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
-
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
HIV treatment and/or prevention
Foreseen user group
To be determined
Foreseen duration between application(s)
To be determined
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
-
Genito-urinary system and sex hormones, Levonorgestrel (LNG), Etonogestrel (ENG), Oxytocin, Testosterone (T)
Class(es)
levonorgestrel, etonogestrel, testosterone, oxytocin, etc.
Development stage
Not provided
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Glucocorticoids, Dexamethasone
Class(es)
Dexamethasone etc.
Development stage
Not provided
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Analgesics, Fentanyl, hydrocodone
Class(es)
Hydrocodone, fentanyl etc.
Development stage
Not provided
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Antiparasitic products, Pyrimethamine, Antimalarials, Proguanil
Class(es)
Pyrimethamine, proguanil etc
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
-
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Malaria treatment and/or prophylaxis
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
to be determined
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
-
Drugs used in diabetes, Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues (GLP-1)
Class(es)
GLP-1 receptor agonist
Development stage
Not provided
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Musculo-skeletal system, Meloxicam
Class(es)
Not provided
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
-
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Targets post-operative pain management in cats
Foreseen user group
**Animal health**
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Anticipated: release of meloxicam for 3 to 5 days after a single subcutaneous injection
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
-
Patent info
Technology patent families
Patent informations
| Patent description | Representative patent | Categories | Patent holder | Licence with MPP | Patent source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hydrogel composite depot formulation
Expiry date: 2036-10-21 This invention relates to a depot formulation comprising a biodegradable silica hydrogel composite incorporating a nucleotide or nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitor, wherein the silica hydrogel composite is obtainable by mixing silica particles comprising said nucleotide or nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitor and having a maximum diameter of ≤ 1 000 μm, as such or as a suspension, with silica sol wherein the hydrogel composite is non-flowing and structurally stable when stored at rest and shear-thinning when shear stress is applied by injection. The present invention also relates to use of the depot formulation for treatment of chronic viral infections and prevention of chronic viral reinfection. The present invention further relates to a prefilled syringes comprising said depot formulation. |
WO2017068245 | DELSITECH OY | No | MPP search |
Patent status
| Patent status/countries | Low, Low- middle and upper-middle | High income |
|---|---|---|
| Granted | China, Türkiye, Moldova, Republic of, Mexico, South Africa, India, Brazil | Australia, Liechtenstein, Italy, Norway, Denmark, Belgium, United Kingdom, Greece, Netherlands, Hungary, Croatia, Switzerland, Spain, Austria, Romania, Finland, France, Bulgaria, Poland, Latvia, Ireland, Germany, Portugal, Czechia, Lithuania, Sweden, Japan, Korea, Republic of, United States of America |
| Filed | Canada | |
| Not in force | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Morocco, Albania, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Malta, San Marino, Slovenia, Iceland, Cyprus, Slovakia, Estonia, Luxembourg, Monaco |
MPP Licence(s)
Patent informations
| Patent description | Representative patent | Categories | Patent holder | Licence with MPP | Patent source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Silica Hydrogel Composite
Expiry date: 2034-06-18 This invention relates to a silica hydrogel composite obtainable by mixing silica particles, comprising an encapsulated agent, with a silica sol, wherein obtained hydrogel composite is shear-thinning. The present invention also relates to use of the silica hydrogel composite according to the invention for an injectable, flowing or extrudable formulation. The present invention further relates to a method for preparing the silica hydrogel. |
WO2014207304 | DELSITECH OY | No | Company |
Patent status
| Patent status/countries | Low, Low- middle and upper-middle | High income |
|---|---|---|
| Granted | China, Türkiye | Australia, Canada, Liechtenstein, Italy, Norway, Denmark, Belgium, United Kingdom, Greece, Netherlands, Hungary, Croatia, Switzerland, Spain, Austria, Romania, Finland, France, Bulgaria, Poland, Latvia, Ireland, Germany, Portugal, Czechia, Lithuania, Sweden, Japan, United States of America |
| Filed | ||
| Not in force | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Albania, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Malta, San Marino, Slovenia, Iceland, Cyprus, Slovakia, Estonia, Luxembourg, Monaco |
MPP Licence(s)
Patent informations
| Patent description | Representative patent | Categories | Patent holder | Licence with MPP | Patent source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Method for preparing silica compositions, silica compositions and uses thereof
Expiry date: 2028-02-22 The invention relates to a method for producing a flowing silica composition comprising a sol-gel transfer, wherein redispersion is carried out. The redispersion comprises adding, after having reached gel point of said sol-gel transfer, liquid into the gel formed by the sol-gel transfer, and the adding being made within a sufficiently short time period after reaching the gel point, to result, after mixing to follow of the gel and the liquid, in a rheologically homogenous flowing silica composition, which is and remains injectable as such, or by short stirring < 30 s, through a thin 22G needle. The present invention also relates to flowing silica compositions and gels obtainable by methods of the invention. The present invention further relates to uses of flowing silica compositions |
WO2008104635 | DELSITECH OY | No | Company |
Patent status
| Patent status/countries | Low, Low- middle and upper-middle | High income |
|---|---|---|
| Granted | Serbia | Canada, Liechtenstein, Denmark, United Kingdom, Netherlands, Switzerland, Finland, France, Germany, Sweden |
| Filed | ||
| Not in force | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Türkiye, North Macedonia | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Australia, Italy, Norway, Malta, Belgium, Greece, Hungary, Croatia, Spain, Slovenia, Austria, Romania, Iceland, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Poland, Latvia, Ireland, Estonia, Luxembourg, Portugal, Czechia, Lithuania, Monaco, United States of America |
MPP Licence(s)
Supporting material
Publications
<p><a href="https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28752299/" rel="noopener noreferrer" target="_blank">Silica microparticles for sustained zero-order release of an anti-CD40L antibody. </a></p><p>Tyagi P, Koskinen M, Mikkola J, Leino L, Schwarz A. </p><p>Drug Deliv Transl Res. </p><p>2018 Apr;8(2):368-374. doi: 10.1007/s13346-017-0408-1. PMID: 28752299.</p>
Silica microparticle hydrogel depot (HG) formulation was prepared using spray drying of silica-based sol-gels for the sustained delivery of MR1 antibody which binds to CD40 ligand (CD40L). The formulation was tested in vitro for antibody release, surface morphology, particle size, rheology, and injectability. In vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation was performed for the microparticle formulation and free MR1 antibody in BALB/c female mice. Serum samples up to day 62 were assessed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In vitro release indicated that the MR1 antibody was uniformly encapsulated in silica microparticles, and less than 5% burst release of the antibody was observed. In vivo pharmacokinetics showed a zero-order release up to 62 days from the MR1 silica microparticle HG-controlled release composition.
Keywords: Antibody; Biologics; Silica microparticles; Sustained release.
<p><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8233906/#:~:text=In%20vivo%20pharmacokinetics%20showed%20that,as%20the%20Pamorelin%C2%AE%20injections." rel="noopener noreferrer" target="_blank">Sustained In-Vivo Release of Triptorelin Acetate from a Biodegradable Silica Depot: Comparison to Pamorelin® LA</a></p><p>Nanomedicines, June 2021</p><p>Ari-Pekka Forsback, Panu Noppari, Jesse Viljanen, Jari Mikkola, Mika Jokinen, Lasse Leino, Simon Bjerregaard, Camilla Borglin and Janet Halliday </p>
Triptorelin acetate was encapsulated into silica microparticles by spray-drying a mixture of colloidal silica sol and triptorelin acetate solution. The resulting microparticles were then combined with another silica sol containing silica nanoparticles, which together formed an injectable silica-triptorelin acetate depot. The particle size and surface morphology of the silica-triptorelin acetate microparticles were characterized together with the in vitro release of triptorelin, injectability and rheology of the final injectable silica-triptorelin acetate depot. In vivo pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the silica-triptorelin acetate depot and Pamorelin® were evaluated and compared in Sprague-Dawley male rats after subcutaneous administration. Serum samples up to 91 days were collected and the plasma concentrations of triptorelin and testosterone were analyzed with ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). In vivo pharmacokinetics showed that injections of the silica-triptorelin acetate depot gave 5-fold lower Cmax values than the corresponding Pamorelin® injections. The depot also showed a comparable sustained triptorelin release and equivalent pharmacodynamic effect as the Pamorelin® injections. Detectable triptorelin plasma concentrations were seen with the depot after the 91-day study period and testosterone plasma concentrations remained below the human castration limit for the same period.
Additional documents
Useful links
Access principles
|
|
Collaborate for developmentConsider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology Agree |
|
|
Share technical information for match-making assessmentProvide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit Agree |
|
|
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICsIn the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing Agree |
Comment & Information
More information available at https://www.delsitech.com/
Illustrations

Image of the injection
DelSiTech

SEM images of silica-triptorelin acetate microparticles (magnification 5000×)
Copyright © 2021 by the authors of Forsback et al., Nanomedicines, 2021doi: 10.3390/nano11061578