
|
Developed by 

|
Supported by 

|
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Implant (VitalDose®)
Developer(s)

|
Celanese Corporation Originator
https://www.celanese.com/
United States of America Celanese Corporation, formerly known as Hoechst Celanese, is an American technology and specialty materials company headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is one of the leading global producers of high-performance engineered polymers that are used in a variety of high-value applications. |
Sponsor(s)
|
No sponsor indicated |
Partnerships

|
Population Council https://popcouncil.org/ |

|
Bachem, ltd https://www.bachem.com/ |

|
Nanoform Finland Ltd https://nanoform.com/en/ |

|
Glaukos Corporation https://www.glaukos.com/en-uk/ |

|
Alessa Therapeutics, Ltd https://alessatherapeutics.com/ |

|
John Hopkins University https://www.jhu.edu/ |

|
The Gates Foundation https://www.gatesfoundation.org/ |
Technology information
Type of technology
Polymeric implant
Administration route
Intratumoral, ocular insert, intrathecal, Subcutaneous, Intra-vitreal, Topical (Vaginal), Transdermal
Development state and regulatory approval
travoprost
Marketed
Approved by USFDA on 14 December 2023 for open-angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT)
Description
VitalDose is a polymer-based microporous long-acting implant for systemic and local drug delivery. It has a high drug-loading capacity and supports small molecules, peptides, monoclonal antibodies, and iRNA therapeutics. The implant maintains plasma concentrations for months to years, depending on the API’s pharmacokinetics. Available in rod, ring, and film configurations, it enables versatile clinical applications.
Technology highlight
1) Contraceptive Sustained Release implant (6 months-5 years) 2) Biodurable design made using hydrophobic polymer 3) Customizable design 4) <70% API loading 5) Zero Order Kinetics 6) Refillable, replaced and retrieved 7) Low off-targeting toxicities 8) 40% vinyl acetate serves as a drug matrix while 18% vinyl acetate forms the rate control membrane
Technology main components
1. Polymer Matrix (30–100 wt%) – Core polymers include poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), polyolefins, polyvinyl chloride, polycarbonates, polysulfones, styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers, polyurethanes, silicone polyether-urethanes, polycarbonate urethanes, and silicone polycarbonate-urethanes. Example: Ateva 4030AC. 2. Excipients—Radiocontrast agents, hydrophilic compounds, bulking agents, plasticizers, surfactants, crosslinking agents, flow aids, colorizing agents (e.g., chlorophyll, methylene blue), antioxidants, stabilizers, lubricants, antimicrobial agents, and preservatives. 3. Surfactants—One or more nonionic, anionic, and/or amphoteric surfactants. 4. API—Small molecules, proteins, or iRNA therapeutics. 5. Bromelain Powder
Information on the raw materials sourcing, availability and anticipated price
iDose TR 75 mcg intraocular implant is around 13,950 USD/implant
Delivery device(s)
Sterile single-dose Implant inserter
APIs compatibility profile
API desired features
Water-soluble molecules
Water-insoluble molecules
Small molecules
VitalDose EVA implants target specific pharmacological classes, including estrogen hormones, tetracycline antibiotics, and antiviral agents. The platform primarily delivers small molecules acting as allosteric agonists or inhibitors. Therapeutic agents that are used for treating solid tumor, ocular inflammation, glaucoma, psychiatric disorders, and osteoporosis are also targeted for VitalDose EVA implant.
Nucleic acids
Suitable vaccines include whole viral particles, recombinant proteins, subunit proteins (gp41, gp120, gp140), DNA vaccines, plasmids, bacterial vaccines, and polysaccharides such as extracellular capsular polysaccharides, along with other vaccine vectors. Similarly, nucleic acids may include RNA- or DNA-based molecules such as oligonucleotides, aptamers, ribozymes, DNAzymes, and small interfering RNAs (siRNA), including messenger (mRNA), transfer (tRNA), ribosomal (rRNA), and interfering (iRNA) RNAs.
Proteins
Suitable proteins or peptides may include adrenocorticotropic hormone, angiotensin, β-endorphin, bombesin, calcitonin, calcitonin gene-related polypeptide, cholecystokinin-8, colony-stimulating factors, desmopressin, endothelin, enkephalin, erythropoietins, gastrins, glucagon, human atrial natriuretic polypeptide, interferons, insulin, growth factors, growth hormones, luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone, melanocyte-stimulating hormone, muramyl-dipeptide, neurotensin, oxytocin, parathyroid hormone, peptide T, secretin, and somatomedins.
Additional solubility data
Not provided
Additional stability data
Not provided
API loading: Maximum drug quantity to be loaded
50-75 wt%
API co-administration
2 different APIs : Not provided
LogP
Min: -6.9 Max: 5
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Scale-up prospects
Celanese produces 60,000 metric tons of vinyl acetate annually at its Nanjing facility and plans to expand production by 10,000 metric tons per year. Additionally, Celanese and Nanoform are collaborating to enhance biologics delivery through small implants using the VitalDose platform. Meanwhile, Celanese and Glaat Pharmaceuticals have partnered on formulation development and and clinical trial setup.
Tentative equipment list for manufacturing
HAAKE™ Rheomix OS Mixers
Manufacturing
Manufacturing Process of EVA Implants (Hot Melt Extrusion(HME) /Fusion Deposition 3D Modeling) i) Mixing Processes (One or more of the following) 1. Melt mixing 2. Extrusion 3. Batch mixing 4. Roll milling ii) Melt Processing Techniques at 210°C (One or more of the following) 1. Compression molding 2. Injection molding (injection phase and holding phase) 3. Blow molding 4. Vacuum forming 5. Calendaring 6. Extrusion 7. Spinning 9. Film formation The API and ground EVA polymer are dry blended and are fed into HME to yield the final product form.
Specific analytical instrument required for characterization of formulation
UV/Vis absorption spectroscopy using Cary 1 split beam instrument
Clinical trials
GC-010
Identifier
NCT03519386
Link
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03519386
Phase
Phase III
Status
Completed
Sponsor
Glaukos Corporation
More details
Phase III study to compare the safety and efficacy of intraocular implants containing travoprost at two different elution rates versus Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, 0.5% (timolol) in reducing elevated intraocular pressure in subjects with open-angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT).
Purpose
Randomized Study Comparing Two Models of a Travoprost Intraocular Implant to Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, 0.5%
Interventions
Intervention 1
Intervention 2
Countries
Sites / Institutions
Not provided
Trials dates
Anticipated Start Date
Not provided
Actual Start Date
2018-07-26
Anticipated Date of Last Follow-up
2024-11-12
Estimated Primary Completion Date
Not provided
Estimated Completion Date
Not provided
Actual Primary Completion Date
2022-04-05
Actual Completion Date
2024-04-02
Studied populations
Age Cohort
- Adults
- Older Adults
Genders
- All
Accepts pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Accepts lactating individuals
Unspecified
Accepts healthy individuals
No
Comments about the studied populations
Inclusion Criteria: * Diagnosed with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. * C/D ratio ≤ 0.8 * Zero to three preoperative ocular hypotensive medications Exclusion Criteria: * Active corneal inflammation or edema. * Retinal disorders not associated with glaucoma.
Health status
Not provided
Study type
Interventional (clinical trial)
Enrollment
590
Allocation
Randomized
Intervention model
Parallel Assignment
Intervention model description
Not provided
Masking
Double-blind masking
Masking description
Not provided
Frequency of administration
Studied LA-formulation(s)
Studied route(s) of administration
Use case
Treatment
Key resources
IDOS-402-IVIV
Identifier
NCT06582732
Link
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06582732
Phase
Phase II
Status
Completed
Sponsor
Glaukos Corporation
More details
To evaluate the performance of the Travoprost Intracameral Implant by determining residual drug in explanted implants of the Travoprost Intracameral Implant and by determining aqueous humor concentrations of travoprost free acid at specified timepoints post administration through 24 months
Purpose
Performance of the Travoprost Intraocular Implant
Interventions
Intervention 1
Intervention 2
Intervention 3
Intervention 4
Intervention 5
Countries
Sites / Institutions
Not provided
Trials dates
Anticipated Start Date
Not provided
Actual Start Date
2021-03-10
Anticipated Date of Last Follow-up
2024-09-19
Estimated Primary Completion Date
Not provided
Estimated Completion Date
Not provided
Actual Primary Completion Date
2023-11-02
Actual Completion Date
2023-11-02
Studied populations
Age Cohort
- Adults
- Older Adults
Genders
- All
Accepts pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Accepts lactating individuals
Unspecified
Accepts healthy individuals
No
Comments about the studied populations
Inclusion Criteria: * Diagnosis of either open angle glaucoma (i.e. primary, pseudoexfoliation, or pigmentary glaucoma) or ocular hypertenson * Zero to three topical intraocular pressure lowering medications at the time of Visit 1 (Screening) exam. * Best spectacle corrected visual acuity of 16 letters or more correctly read at 4 meters or better in each eye. * Open angle as defined by Shaffer grade ≥ 3 at slit-lamp at the planned implantation site Exclusion Criteria: * Traumatic, uveitic, neovascular, or angle-closure glaucoma; or glaucoma associated with vascular disorders * Active ocular inflammation, infection or edema * Clinically significant dystrophy (e.g., bullous keratopathy, Fuch's dystrophy) or clinically significant guttata
Health status
Not provided
Study type
Interventional (clinical trial)
Enrollment
210
Allocation
Not provided
Intervention model
Sequential assignment
Intervention model description
Not provided
Masking
Open label
Masking description
Not provided
Frequency of administration
Studied LA-formulation(s)
Studied route(s) of administration
Use case
Treatment
Key resources
Excipients
Proprietary excipients used
No proprietary excipient used
Novel excipients or existing excipients at a concentration above Inactive Ingredients Database (IID) for the specified route of administration
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
Residual solvents used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
Other features of the technology
- Biodegradable
- Monolithic
Release properties
VitalDose is a continuous drug delivery system that releases therapeutic agents from an ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) membrane at a steady, low-dose rate, with sustained release lasting up to three years. In intratumoral administration, the drug exhibits modified kinetics, allowing for a gradual and controlled release directly into the tumor microenvironment, optimizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic exposure.
Injectability
VitalDose is a liquid formulation and can be injected using a standard injection device with a standard 21-25 gauge needle or even thinner depending on the formulation characteristics.
Safety
In the Phase 3 clinical trial of iDose, the Travoprost VitalDose implant was evaluated for safety. Among the patients who received the implant, 2.6% experienced systemic serious adverse events (SAEs), while 0.5% experienced ocular SAEs. The most common side effects were iritis, ocular hyperemia, reduced visual acuity, and increased intraocular pressure (IOP).
Stability
The API in the EVA implant demonstrated stability over a period of 6 months.
Storage conditions and cold-chain related features
Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F). Do not freeze
Potential application(s)
Therapeutic area(s)
Use case(s)
Use of technology
Ease of administration
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
Frequency of administration
Monthly, Every 6 months, Yearly
User acceptance
Not provided
Targeted user groups
Age Cohort- Adults
- Older Adults
- Female
- Cisgender female
- Transgender female
- All
Pregnant individuals
No
Lactating individuals
Unspecified
Healthy individuals
Unspecified
Comment
Not provided
Potential associated API(s)
Beta blocking agents
Class(es)
Beta Blocker - Opthalmology
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Glaucoma
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
travoprost
Class(es)
Prostaglandin analogues
Development stage
Marketed
Clinical trial number(s)
NCT03519386
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Open-Angle Glaucoma, Ocular Hypertension
Foreseen user group
Adults < 18years old
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Single dose
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Approved by USFDA on 14 December 2023 for open-angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT)
Dexamethasone
Class(es)
Synthetic Corticosteroids
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Ocular hypertension
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
goserelin
Class(es)
Gonadotropin releasing hormone analogues
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Solid Tumors
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
trastuzumab
Class(es)
HER-2 Inhibitors
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Solid Tumors
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Patent info
Description
Implantable Device for Sustained Release of a Macromolecular Drug Compound
Brief description
An implantable device for delivery of a macromolecular drug compound is provided. The device comprises a core having an outer surface and a membrane layer positioned adjacent to the outer surface of the core. The core comprises a core polymer matrix within which is dispersed a drug compound having a molecular weight of about 0.5 kDa or more, the polymer matrix containing a hydrophobic polymer. Further, the membrane layer comprises a membrane polymer matrix within which the macromolecular drug compound is optionally dispersed. The concentration of the macromolecular drug compound in the core is greater than the concentration of the macromolecular drug compound in the membrane layer.
Representative patent
US20190358167A1
Category
Device
Patent holder
Celanese EVA Performance Polymers Corporation
Exclusivity
Not provided
Expiration date
May 20, 2039
Status
Active
Description
Injection Molded Medical Devices Made From A High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
Brief description
A high molecular weight polyethylene polymer is formulated so that the polymer is capable of being injection molded. The polyethylene polymer has a Viscosity Number of greater than about 400 ml/g and has a melt flow rate of greater than about 0.9 g/10 min. The polyethylene polymer is of high purity and is particularly well suited for producing medical products.
Representative patent
US20240262942A1
Category
Device
Patent holder
Celanese International Corp
Exclusivity
Not provided
Expiration date
Not provided
Status
Pending
Supporting material
Publications
There are no publication
Useful links
There are no additional links
Access principles
|
|
Collaborate for developmentConsider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology Not provided |
|
|
Share technical information for match-making assessmentProvide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit Not provided |
|
|
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICsIn the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing Not provided |
Comment & Information
Illustrations
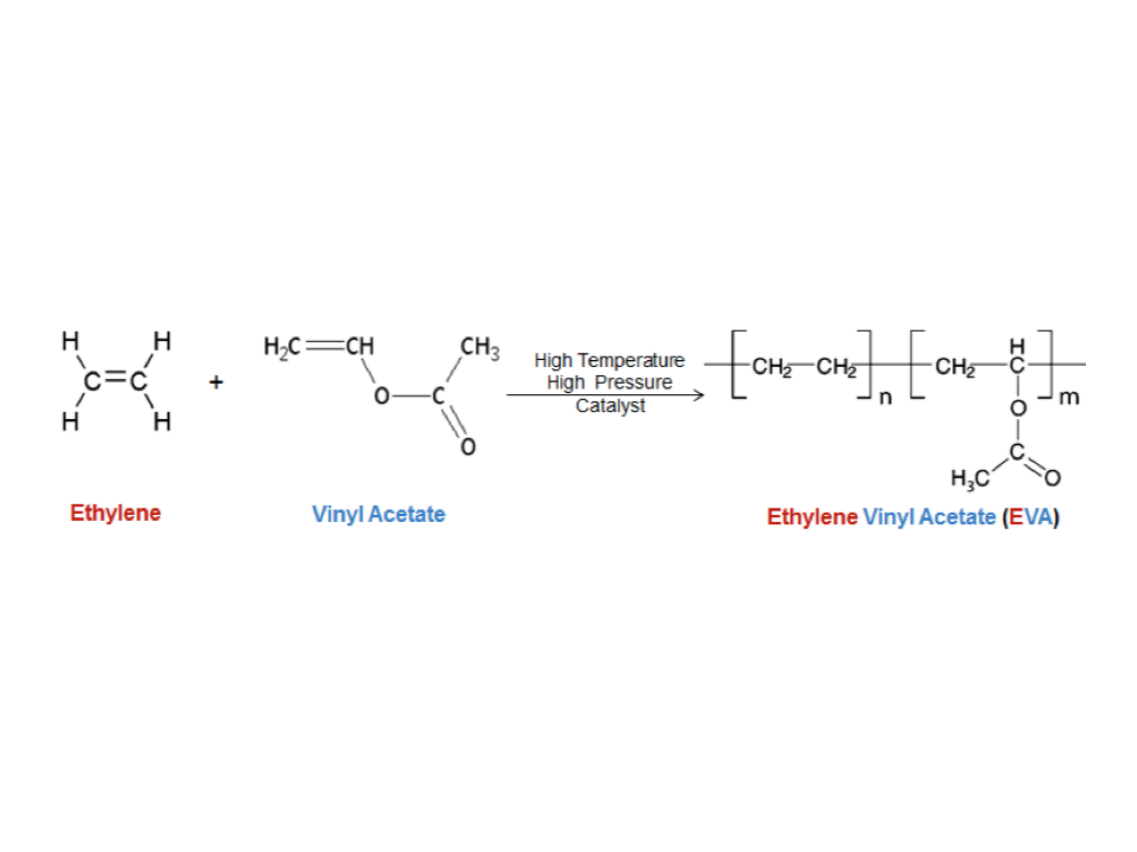
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Synthesis
Zhang, B. (2015). Potential use of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer excipient in oral controlled release applications: A literature review. Celanese. https://www.celanese.com/-/media/eva%20polymers/fi

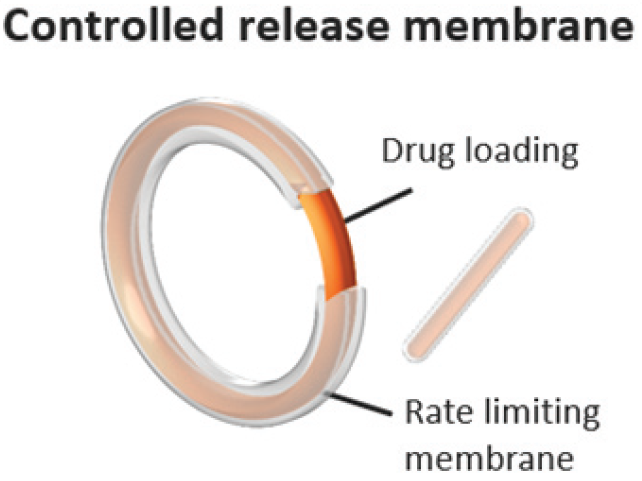
VitalDose EVA Implant with Core layer (reservoir) and a Membrane layer (raye limiting membrane)
Holmes, C., Chen, K., & Duke, B. (n.d.). Drug delivery platform - VitalDose® EVA implants for systemic & local delivery of therapeutics. Celanese. Retrieved from https://www.celanese.com/-/media/eva%2
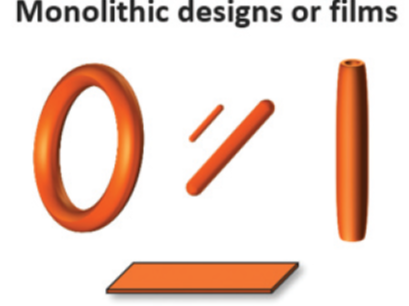
Various Structural forms of EVA implant i.e, rings, rods and films
Holmes, C., Chen, K., & Duke, B. (n.d.). Drug delivery platform - VitalDose® EVA implants for systemic & local delivery of therapeutics. Celanese. Retrieved from https://www.celanese.com/-/media/eva%2
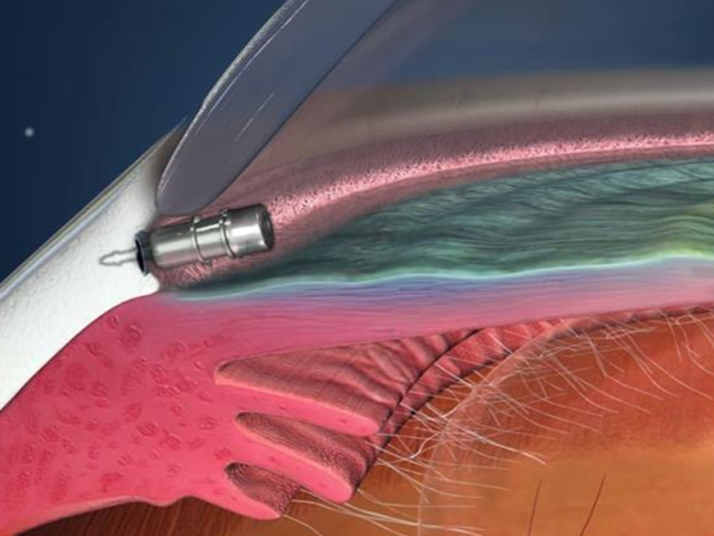
Intracameral VITALDOSE depot of Travoprost
Innovative Glaucoma Solutions. (2024). iDose TR prescribing information. iDose TR. https://www.idosetr.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/iDose-TR-Prescribing-Information.pdf
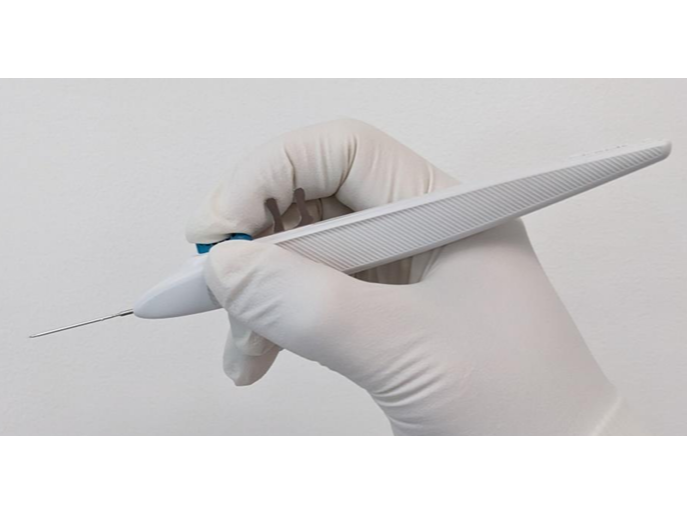
Sterile Single-dose inserter used for intracameral depot adminstration
Innovative Glaucoma Solutions. (2024). iDose TR prescribing information. iDose TR. https://www.idosetr.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/iDose-TR-Prescribing-Information.pdf