
|
Developed by 

|
Supported by 

|
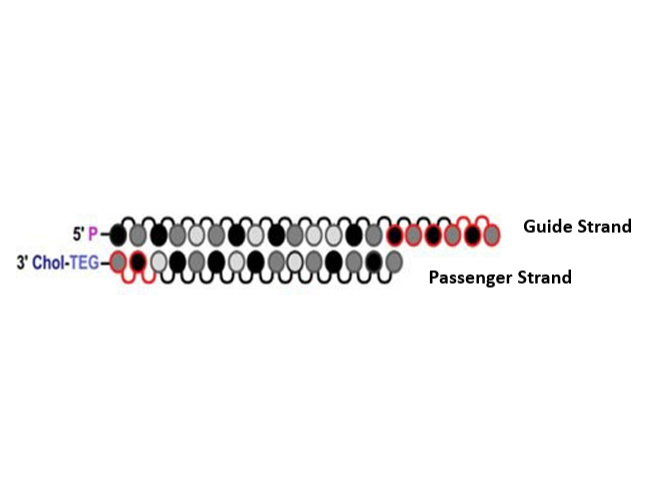
INTASYL self-delivery technology
Developer(s)

|
Phio Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. Originator
https://phiopharma.com/
United States of America Phio Pharmaceuticals, founded in 2011 and headquartered in Marlborough, Massachusetts, is a biotechnology company specializing in RNA-based immuno-oncology therapies. Initially named RXi Pharmaceuticals, it rebranded in 2018 to reflect its focus on self-delivering RNAi technology. The company develops tumor-targeting therapeutics, leveraging cutting-edge RNAi platforms. |
Sponsor(s)

|
Triton Funds https://www.tritonfunds.com/ |
Partnerships

|
Glycostem Ltd. https://www.glycostem.com/ |

|
Helmholtz Zentrum München https://www.helmholtz-munich.de/ |

|
Medigene AG https://medigene.com/ |
Technology information
Type of technology
Chemically modified siRNA for self-delivery
Administration route
Intratumoral, Intra-vitreal
Development state and regulatory approval
PH-762
Phase I
FDA has cleared the IND application for PH-762
Description
INTASYL™ Technology is a proprietary self-delivering RNA interference (sd-rxRNA®) platform designed for precise gene silencing in immuno-oncology. Unlike traditional RNAi therapies, INTASYL allows direct cellular uptake without requiring complex delivery systems. Engineered for immune cells, it enhances anti-tumor responses while ensuring safety, stability, and efficiency. The sd-rxRNA molecules are chemically modified with hydrophobic and hydrophilic elements, enabling passive diffusion into cells. These modifications also provide stability and resist disintegration.
Technology highlight
1. Chemically modified siRNA structure and self-delivery system 2. Cellular uptake mechanism via direct membrane penetration 3. Intracellular processing and RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) Activation 4. Gene silencing and Immuno-oncology applications 5. Target specificity
Technology main components
Chemically modified siRNA
Information on the raw materials sourcing, availability and anticipated price
Not provided
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
API desired features
Proteins
INTASYL self-delivery technology utilizes siRNA to specifically target and silence a range of immuno-oncology proteins, including PD-1, BRD4, CTLA4, TIGIT, LAG3, TIM3, CBLB, SHP-1, STAT-3, MDM2, ADORA2, MMP-1, CD96, CISH, CSK, DGKα, DGKζ, DNMT3A, HK2, IL-6, KLRC1, PD-L1, PRDM, PTEN, TBX21, TET2, and other related proteins involved in immune regulation and tumor evasion. Additionally, it targets dermatology-related proteins such as CTGF, COX2, TGFB1, TGFB2, SPP1, TYR, and MMP1, as well as BRD4, contributing to therapeutic strategies in both immuno-oncology and dermatological conditions.
Additional solubility data
Not provided
Additional stability data
Not provided
API loading: Maximum drug quantity to be loaded
75-90 wt%
API co-administration
2 different APIs : Two APIs should target different genes simultaneously
LogP
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Scale-up prospects
Not provided
Tentative equipment list for manufacturing
Mermade 12 DNA/RNA Synthesizer
Manufacturing
Manufacturing Process of INTASYL (cGMP): 1. Oligonucleotide Synthesis (via Mermade 12 DNA/RNA Synthesizer) 2. Cleavage and Deprotection 3. Purification (via ion exchange chromatography) 4. Sense Strand Purification 5. Desalting and Concentration 6. Analysis by HPLC and ESI-MS.
Specific analytical instrument required for characterization of formulation
1. HPLC analysis on a Shimadzu Prominence system. 2. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) analysis using Promass Deconvolution for Xcalibur.
Clinical trials
PHIO-762-2301
Identifier
NCT06014086
Link
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06014086
Phase
Phase I
Status
Recruiting
Sponsor
Phio Pharmaceuticals Inc.
More details
The goal of this clinical trial is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of intratumoral injections of PH-762 in squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, or Merkel cell carcinomas of the skin, to understand what the body does to the PH-762, and to observe how the tumor responds to the drug. Participants will receive four injections of PH-762 at weekly intervals, into a single tumor, followed by surgical removal of the tumor approximately two weeks later.
Purpose
Intratumoral PH-762 for Cutaneous Carcinoma
Interventions
Intervention 1
Countries
Sites / Institutions
Not provided
Trials dates
Anticipated Start Date
Not provided
Actual Start Date
2023-11-07
Anticipated Date of Last Follow-up
2025-01-24
Estimated Primary Completion Date
2025-06-01
Estimated Completion Date
2025-09-01
Actual Primary Completion Date
Not provided
Actual Completion Date
Not provided
Studied populations
Age Cohort
- Adults
- Older Adults
Genders
- All
Accepts pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Accepts lactating individuals
Unspecified
Accepts healthy individuals
No
Comments about the studied populations
Key Inclusion Criteria: * Histologically confirmed cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), melanoma, or Merkel cell carcinoma, meeting one of the following criteria: * cSCC, resectable local tumors: must be Stage II or lower, amenable to curative resection and in a location where acceptable surgical margins are anticipated * cSCC, unresectable local tumors: must be Stage II or lower, tumor has been unresponsive to prior radiation therapy or is not a candidate for curative radiation therapy * cSCC, metastatic disease: disease has progressed during or following prior checkpoint inhibitor therapy (anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibody) * Melanoma, metastatic disease: Stage IV disease with a cutaneous lesion that has progressed during or following checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Health status
Not provided
Study type
Interventional (clinical trial)
Enrollment
30
Allocation
Not provided
Intervention model
Single group assignment
Intervention model description
Not provided
Masking
Open label
Masking description
Not provided
Frequency of administration
Studied LA-formulation(s)
Studied route(s) of administration
Use case
Treatment
Key resources
RXI-109-1501
Identifier
NCT02599064
Link
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02599064
Phase
Phase I/II
Status
Unknown status
Sponsor
RXi Pharmaceuticals, Corp.
More details
This study is designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and clinical activity of RXI-109 administered by intravitreal injection to reduce the progression of subretinal fibrosis in subjects with advanced neovascular age-related macular degeneration (NVAMD).
Purpose
Evaluating RXI-109 to Reduce the Progression of Subretinal Fibrosis in Subjects With NVAMD
Interventions
Intervention 1
Countries
Sites / Institutions
Not provided
Trials dates
Anticipated Start Date
Not provided
Actual Start Date
2015-11-01
Anticipated Date of Last Follow-up
2018-02-22
Estimated Primary Completion Date
2018-04-01
Estimated Completion Date
2018-05-01
Actual Primary Completion Date
Not provided
Actual Completion Date
Not provided
Studied populations
Age Cohort
- Adults
- Older Adults
Genders
- All
Accepts pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Accepts lactating individuals
Unspecified
Accepts healthy individuals
No
Comments about the studied populations
Inclusion Criteria: * Subjects presenting with advanced NVAMD in the study eye with BCVA ≤20/100 potentially due to subretinal fibrosis involving the fovea * BCVA ≥20/800 in the contralateral eye and better than the study eye * ≥50 years of age * Subfoveal choroidal neovascularization (CNV) of any type Exclusion Criteria: * Presence of other causes of CNV including pathologic myopia, ocular histoplasmosis syndrome, angioid streaks, choroidal rupture, and multifocal choroiditis * Evidence of inflammation (Grade 1 or higher) in the anterior or posterior chamber.
Health status
Not provided
Study type
Interventional (clinical trial)
Enrollment
Not provided
Allocation
Not provided
Intervention model
Single group assignment
Intervention model description
Not provided
Masking
Open label
Masking description
Not provided
Frequency of administration
Studied LA-formulation(s)
Studied route(s) of administration
Use case
Treatment
Key resources
Excipients
Proprietary excipients used
No proprietary excipient used
Novel excipients or existing excipients at a concentration above Inactive Ingredients Database (IID) for the specified route of administration
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
Residual solvents used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
Other features of the technology
Not provided
Release properties
When the INSTACYL formulation is administered locally, i.e., intratumorally, the chemically modified siRNA undergoes spontaneous cellular uptake due to the interaction of the lipophilic functional group (e.g., sterol group) with the cell membrane. Thus, the cellular uptake of INSTACYL does not require facilitated transport systems or carriers.
Injectability
INSTACYL formulation is designed for intratumoral and intravitreal route of adminstration.
Safety
The INSTACYL products were well tolerated in the clinical phase 1 studies. One of such study on PH-762 once weekly (for 4 weeks) indicate that there was no No dose-limiting toxicities or clinically significant treatment-emergent adverse effects have been reported.
Stability
Not provided
Storage conditions and cold-chain related features
Not provided
Potential application(s)
Therapeutic area(s)
Use case(s)
Use of technology
Ease of administration
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
Frequency of administration
Weekly
User acceptance
Not provided
Targeted user groups
Age Cohort- Adults
- Older Adults
- All
Pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Lactating individuals
Unspecified
Healthy individuals
Unspecified
Comment
Not provided
Potential associated API(s)
PH-762
Class(es)
PD-1 protein silencer
Development stage
Phase I
Clinical trial number(s)
NCT06014086
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Cutaneous carcinoma
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Once weekly
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
FDA has cleared the IND application for PH-762
PH-894
Class(es)
BRD4 protein silencer
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Melanoma
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Once weekly
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Patent info
Description
Chemically modified oligonucleotides
Brief description
The disclosure relates, in some aspects, to methods and compositions for production of immunogenic compositions. In some embodiments, the disclosure provides host cells which have been treated ex vivo with one or more oligonucleotide agents capable of controlling and/or reducing the differentiation of the host cell. In some embodiments, compositions and methods described by the disclosure are useful as immunogenic modulators for treating cancer.
Representative patent
AU2018313149B2
Category
Not provided
Patent holder
Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp
Exclusivity
Not provided
Expiration date
August 7, 2038
Status
Active
Description
Reduced size self-delivering RNAi compounds
Brief description
A method for delivering a nucleic acid to a remote target tissue in a subject in need thereof, comprising systemically administering to the subject an sd-rxRNA® in an effective amount to promote RNA interference by the sd-rxRNA® in the remote target tissue, wherein the sd-rxRNA® comprises a guide strand and a passenger strand, wherein the sd-rxRNA® includes a double-stranded region and a single stranded region wherein the double stranded region is from 8-15 nucleotides long, wherein the single stranded region is at the 3′ end of the guide strand and is 4-12 nucleotides long, wherein the single stranded region contains 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12 phosphorothioate modifications, wherein at least 40% of the nucleotides of the sd-rxRNA® are modified, and wherein at least two Us.
Representative patent
US10240149B2
Category
Not provided
Patent holder
Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp
Exclusivity
Not provided
Expiration date
March 24, 2031
Status
Active
Description
Phagocytic cell delivery of RNAI
Brief description
The present invention provides a particulate delivery system for delivering an RNAi construct to phagocytic cells such as macrophages, comprising various configurations of a complex comprising a phagocytic cell-targeting moiety and an RNAi construct. The invention further provides methods of making the delivery system, and their uses, such as treating phagocytic cell-associated disease conditions.
Representative patent
US8815818B2
Category
Not provided
Patent holder
Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp
Exclusivity
Not provided
Expiration date
August 16, 2029
Status
Active
Supporting material
Publications
<p><span style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">Maxwell, M., Holton, K., Looby, R. J., Byrne, M., & Cardia, J. (2024). Self-Delivering RNAi Compounds for Reduction of Hyperpigmentation. </span><em style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology</em><span style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">, </span><em style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">17</em><span style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">, 3033–3044. </span><a href="https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S498987" rel="noopener noreferrer" target="_blank" style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S498987</a></p>
Purpose: Abnormal melanin synthesis causes hyperpigmentation disorders like melasma and lentigines, impacting psychological well-being. RNA interference (RNAi) uses small RNA molecules to inhibit gene expression by targeting specific mRNA, silencing genes involved in undesirable cellular functions. This study assessed INTASYL compounds, self-delivering RNAi molecules, designed to target and reduce tyrosinase gene expression to decrease pigmentation.
Methods: 36 INTASYL compounds were designed to target and reduce TYR gene expression and tested in a screening assay. RXI-231, the lead compound, was tested in normal human epithelial melanocytes and the MelanoDerm™ model, a 3D reconstituted human epidermal culture. RXI-231 was evaluated for its ability to reduce tyrosinase mRNA expression, in vitro dopachrome formation, and melanin content. Penetration of fluorescently labeled INTASYL compounds through the stratum corneum into the epidermis was tested in cultured porcine skin explants using a DermaPen® microneedle device and a proprietary mixture of penetration enhancers. RXI-231 was also tested for skin irritation in the MatTek EpiDerm™ model to determine its non-irritant profile.
Results: RXI-231 significantly reduced tyrosinase mRNA expression, dopachrome formation, and melanin content in both normal human melanocytes and the MelanoDerm model. Application of INTASYL compounds every other day visibly reduced pigmentation in the 3D epidermal cultures. Penetration studies showed efficient delivery into the epidermis, overcoming the stratum corneum barrier. RXI-231 showed no irritation, with viability above 50% in the MatTek EpiDerm model, confirming its non-irritant profile.
<p><span style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">Cuiffo, B., Maxwell, M., Yan, D., Guemiri, R., Boone, A., Bellet, D., Rivest, B., Cardia, J., Robert, C., & Fricker, S. P. (2024). Self-delivering RNAi immunotherapeutic PH-762 silences PD-1 to generate local and abscopal antitumor efficacy. </span><em style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">Frontiers in immunology</em><span style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">, </span><em style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">15</em><span style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">, 1501679. </span><a href="https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501679" rel="noopener noreferrer" target="_blank" style="color: rgb(33, 33, 33);">https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501679</a></p>
Objective: Immunotherapeutic inhibition of PD-1 by systemically administered monoclonal antibodies is widely used in cancer treatment, but it may cause severe immune-related adverse events (irSAEs). Neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibition before surgery has shown promise in reducing recurrence by stimulating durable antitumor immunity. Local intratumoral (IT) immunotherapy is a potential strategy to minimize irSAEs, but antibodies have limited tumor penetration, making them less suitable for this approach. Therapeutic self-delivering RNAi (INTASYL) is an emerging modality well-suited for neoadjuvant immunotherapy. This study presents preclinical proof-of-concept for PH-762, an INTASYL designed to silence PD-1, currently in clinical development for advanced cutaneous malignancies (ClinicalTrials.gov#NCT06014086).
Methods and analysis: PH-762 pharmacology was characterized in vitro, and in vivo antitumor efficacy was evaluated using a murine analogue (mPH-762) in syngeneic tumor models with varying PD-1 responsiveness. Bilateral Hepa1-6 models assessed abscopal effects of local treatment. Ex vivo analyses explored mechanisms of direct and abscopal efficacy.
Results: PH-762 was rapidly internalized by human T cells, silencing PD-1 mRNA and decreasing PD-1 surface protein, enhancing TCR-stimulated IFN-γ and CXCL10 secretion. In vivo, IT mPH-762 provided robust antitumor efficacy, local and lymphatic biodistribution, and was well tolerated. Ex vivo analyses revealed that IT mPH-762 depleted PD-1 protein, promoted leukocyte and T cell infiltration, and correlated with tumor control. IT mPH-762 also demonstrated efficacy against untreated distal tumors (abscopal effect) by priming systemic antitumor immunity.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
There are no additional links
Access principles
|
|
Collaborate for developmentConsider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology Not provided |
|
|
Share technical information for match-making assessmentProvide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit Not provided |
|
|
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICsIn the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing Not provided |
Comment & Information
Illustrations

Guide strand acts as active strand with RISC and the passenger strand is inactive but plays a role in structural integrity.
Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp. (2025). Phio Pharmaceuticals: INTASYL® siRNA Patented Technology. https://d2ghdaxqb194v2.cloudfront.net/2839/196675.pdf
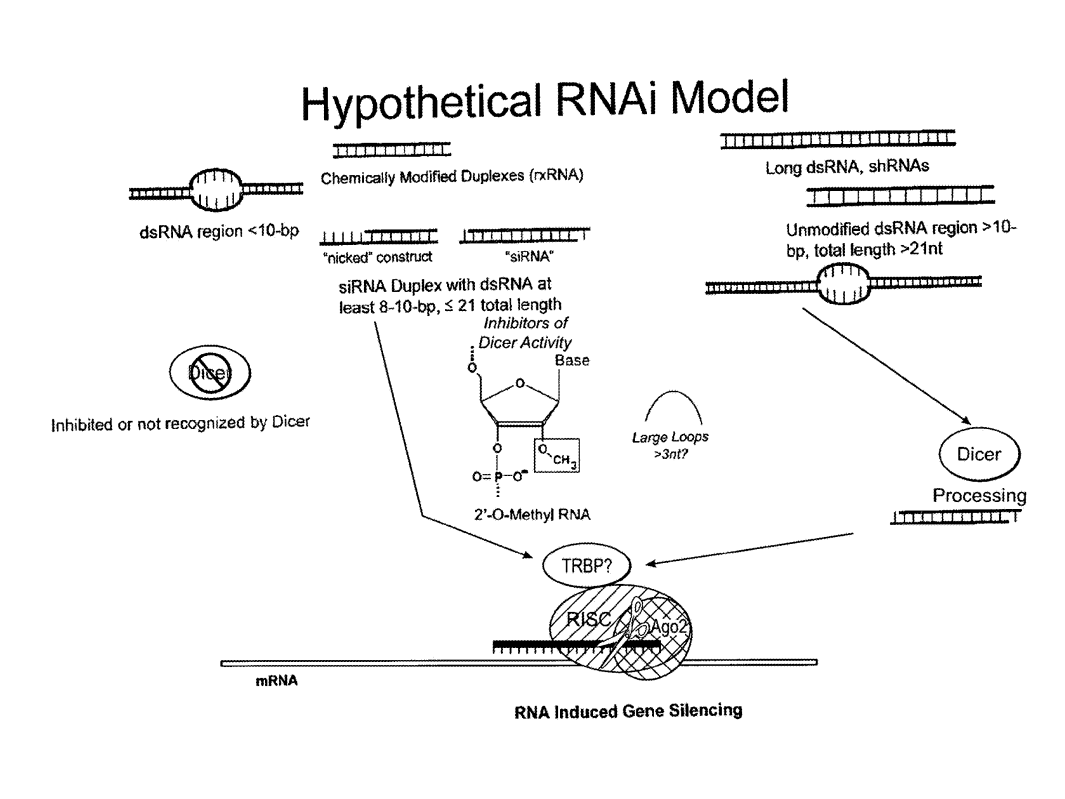
Example of RNAi model and its mechanism of action
Ehrlich, G., & Fenster, M. (2021). Methods and systems for anonymously selecting subjects for treatment against an infectious disease caused by a pathogen. U.S. Patent No. US20210147849A1.