
|
Developed by 

|
Supported by 

|

SAFA (anti-Serum Albumin Fab Associated) platform technology
Developer(s)

|
AprilBio Originator
http://www.aprilbio.com/
South Korea AprilBio is a South Korean biopharmaceutical company that is based at Gangwon University, developing specialized biologics and antibody drugs for rare diseases, oncology, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Their focus areas include rare diseases, oncology, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. |
Sponsor(s)

|
Yuvan, USA https://www.yuhan-usa.com/ |
Partnerships

|
Evoimmune https://www.evommune.com/ |

|
Lundbeck https://www.lundbeck.com/uk |
Technology information
Type of technology
Fusion of a therapeutic protein with a human antibody engineered to bind albumin.
Administration route
Intravenous
Development state and regulatory approval
APB-A1 (anti-CD40L agent)
Phase I
Not provided
Description
SAFA (anti-Serum Albumin Fab-Associated) is a novel technology that modifies antiserum albumin Fab fragments to create long-acting therapeutic proteins. This modified fab can be fused with antibody fragments and/or recombinant proteins. These fused constructs, termed SAFAbodies, exhibit high affinity binding to natural serum proteins. At the cellular level, these SAFAbodies bind to neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn) to avoid degradation. This FcRn binding mechanism results in the prolonged action of the SAFA formulation i.e., prolonged half-life and targeted site of action.
Technology highlight
1) Prolonged Half-Life 2) Targeted Site of Action 3) No chemical conjugated with PEG or any other polymer 4) Flexibility in choosing protein expression system 6) Less immunogenic side effects due to no/low Fc gamma receptor (FcgR) interaction.
Technology main components
1) Genetically Modified Albumin Fusion protein 2) API 3) FcRN4 4) Excipients such as fillers, antiagglutinating agents, lubricating agents, wetting agents, flavoring agents, emulsifiers, and preservatives are added based on the API.
Information on the raw materials sourcing, availability and anticipated price
Not provided
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
API desired features
Proteins
Therapeutic proteins such as Monoclonal Antibodies, Interleukins, CD-40, Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) analogues, Human Growth Hormone (HGH), IFN-β (Interferon Beta), checkpoint inhibitors, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) analogues, and GLP-2 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-2) are targeted
Additional solubility data
Not provided
Additional stability data
Not provided
API loading: Maximum drug quantity to be loaded
75-90 wt%
API co-administration
1 single API :
LogP
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Scale-up prospects
Not provided
Tentative equipment list for manufacturing
Not provided
Manufacturing
The manufacturing process of the SAFA formulation involves the following key steps: • Generation of SL33X-API Fusion Constructs: This step is performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification followed by cloning techniques to produce the desired constructs. • Preparation of Soluble Fab Fragments and SL33X-API Fusion Proteins: Soluble Fab fragments and fusion proteins are synthesized and purified as part of the formulation process. Note: The complete manufacturing process for the finalized product remains undisclosed.
Specific analytical instrument required for characterization of formulation
• Differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) • Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) • In vitro bioactivity assay • UV Spectrometer (Bio-Rad) • Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blot analyses (using Coomassie Blue staining)
Clinical trials
APB-R3-101
Identifier
NCT05715736
Link
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05715736
Phase
Phase I
Status
Completed
Sponsor
Syneos Health
More details
This will be a single centre, Phase 1, First-In-Human, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Single Ascending Dose of APB-R3 in Healthy Participants.
Purpose
Assessment of Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of APB-R3
Interventions
Intervention 1
Intervention 2
Countries
Sites / Institutions
Not provided
Trials dates
Anticipated Start Date
Not provided
Actual Start Date
2023-03-08
Anticipated Date of Last Follow-up
2024-01-04
Estimated Primary Completion Date
Not provided
Estimated Completion Date
Not provided
Actual Primary Completion Date
2023-12-19
Actual Completion Date
2023-12-19
Studied populations
Age Cohort
- Adults
Genders
- All
Accepts pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Accepts lactating individuals
Unspecified
Accepts healthy individuals
Yes
Comments about the studied populations
Inclusion Criteria: 1. Male or female, non-smoker, 18 to 60 years of age (both inclusive), 2. Healthy as defined by: 1. the absence of clinically significant illness and surgery within 4 weeks prior to study drug administration in the opinion of the investigator. 2. the absence of clinically significant history of neurological, endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, hematological, immunological, psychiatric, gastrointestinal, renal, hepatic, and metabolic disease in the opinion of the investigator. Exclusion Criteria: 1. Abnormal finding at physical examination 2. Evidence of clinical significant hepatic or renal impairment 3. Clinically significant abnormal laboratory test results or positive serology test results for HBsAg, HCV antibody, or HIV antigen and antibody.
Health status
Not provided
Study type
Interventional (clinical trial)
Enrollment
31
Allocation
Randomized
Intervention model
Sequential assignment
Intervention model description
Not provided
Masking
Quadruple-blind masking
Masking description
Not provided
Frequency of administration
Studied LA-formulation(s)
Studied route(s) of administration
Use case
Treatment
Key results
20119A
Identifier
NCT05136053
Link
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05136053
Phase
Phase I
Status
Completed
Sponsor
H. Lundbeck A/S
More details
The main goal of this study is to learn more about the safety of a drug called Lu AG22515. During the trial, healthy adult participants will receive a single dose of Lu AG22515 or a placebo (normal saline solution).
Purpose
A Study Investigating Lu AG22515 in Healthy Adults
Interventions
Intervention 1
Intervention 2
Intervention 3
Countries
Sites / Institutions
Not provided
Trials dates
Anticipated Start Date
Not provided
Actual Start Date
2022-03-18
Anticipated Date of Last Follow-up
2023-08-24
Estimated Primary Completion Date
Not provided
Estimated Completion Date
Not provided
Actual Primary Completion Date
2023-08-05
Actual Completion Date
2023-08-05
Studied populations
Age Cohort
- Adults
Genders
- All
Accepts pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Accepts lactating individuals
Unspecified
Accepts healthy individuals
Yes
Comments about the studied populations
Inclusion Criteria: * Body mass index (BMI) ≥18.0 and ≤32.0 kilograms (kg)/square meter (m\^2) and weight between 55 and 110 kg (both inclusive) at screening. * Fully vaccinated against COVID-19, as evidenced by presentation of a vaccine card. The last administration of the COVID-19 vaccination must be received a minimum of 30 days and maximum 6 month prior to dosing in this study. * Medically healthy with no clinically significant medical history, physical examination and neurological assessment, laboratory profiles, vital signs, or electrocardiograms (ECGs), as deemed by the principal investigator (PI) or designee.
Health status
Not provided
Study type
Interventional (clinical trial)
Enrollment
58
Allocation
Randomized
Intervention model
Sequential assignment
Intervention model description
Not provided
Masking
Double-blind masking
Masking description
Not provided
Frequency of administration
Studied LA-formulation(s)
Studied route(s) of administration
Use case
Treatment
Key results
Excipients
Proprietary excipients used
No proprietary excipient used
Novel excipients or existing excipients at a concentration above Inactive Ingredients Database (IID) for the specified route of administration
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
Residual solvents used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
Other features of the technology
- Room temperature storage
- At least 1 year shelf life
- Other(s)
Drug release from the protein fragments at intercellular level
Release properties
The antigen-binding fragment (Fab) of the API specifically binds to albumin, enhancing protein binding and thereby extending the API’s half-life (~19 days), volume of distribution at steady state (Vss), and systemic clearance (CL). The prolonged release mechanism involves FcRn-mediated recycling of the Fab-albumin complex at the cellular level, resulting in the slow, sustained release of the API from the complex.
Injectability
SAFA injections are administered via subcutaneous route of administration using a standard 21-gauge needle or even thinner depending on the formulation characteristics.
Safety
Preclinical animal studies show that the 4-week repeated dose toxicity revealed no abnormal toxicological symptoms.
Stability
The shelf life of the SAFA is approximately one year, with a serum stability of the SAFA-coordinated complex lasting 16 days.
Storage conditions and cold-chain related features
Room temperature storage is possible.
Potential application(s)
Therapeutic area(s)
Use case(s)
Use of technology
Ease of administration
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
Frequency of administration
Weekly, Monthly
User acceptance
Not provided
Targeted user groups
Age Cohort- Adults
- Older Adults
- All
Pregnant individuals
Unspecified
Lactating individuals
Unspecified
Healthy individuals
Unspecified
Comment
Not provided
Potential associated API(s)
Interleukins
Class(es)
IL-18 inhibitor
Development stage
Phase I
Clinical trial number(s)
NCT05715736
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Auto-inflammatory diseases and Still's disease
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Cytokines agonists
Class(es)
Anticancerous agent
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Solid Tumors
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Interleukins
Class(es)
IL-2R inhibitor
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Autoimmune diseases
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues (GLP-1)
Class(es)
GLP-1R agonist (antiobesity agent)
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Obesity
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
APB-R6 (TSHR analog)
Class(es)
Anterior Pituitary Hormone receptor analogues
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Endocrine Disorders
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
APB-R2 (FSHR analog)
Class(es)
Anterior Pituitary Hormone Receptor analogues
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Male Infertility
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
APB-A1 (anti-CD40L agent)
Class(es)
Immunosuppressants
Development stage
Phase I
Clinical trial number(s)
NCT05136053
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Autoimmune diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome or organ transplantation
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Every 2 to 4 weeks
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Patent info
Description
Anti - Serum Albumin Fab - Effector Moiety Fusion Construct And A Method Of Preparing The Construct
Brief description
The present invention relates to antigen-binding fragment (Fab) and a Fab-effector fusion protein or (poly)peptide comprising thereof. The Fab of the present invention specifically binds to serum albumin and thereby has extended in vivo half-life. The Fab of the present invention is characterized by not having cysteine residues that are responsible for the interchain disulfide bond in CH1 domain and CκL domain as well. The Fab-effector fusion protein or (poly)peptide of the present invention can be produced in periplasm of E. coli with high yield, and has increased in vivo half-life. Further, the present invention provides E. coli strain which produces various kinds of Fab-effector fusion proteins or (poly)peptides, pharmaceutical composition comprising the fab-effector fusion proteins.
Representative patent
US9879077B2
Category
Formulation
Patent holder
Aprilbio Co Ltd
Exclusivity
Not provided
Expiration date
August 29, 2034
Status
Anticipated expiration
Supporting material
Publications
<p><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">Kang, H. J., Kim, H. J., Jung, M. S., Han, J. K., & Cha, S. H. (2017). Optimal expression of a Fab-effector fusion protein in Escherichia coli by removing the cysteine residues responsible for an interchain disulfide bond of a Fab molecule. </span><em style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">Immunology Letters</em><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">, </span><em style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">184</em><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">, 34-42.</span></p>
Development of novel bi-functional or even tri-functional Fab-effector fusion proteins would have a great potential in the biomedical sciences. However, the expression of Fab-effector fusion proteins in Escherichia coli is problematic especially when a eukaryotic effector moiety is genetically linked to a Fab due to the lack of proper chaperone proteins and an inappropriate physicochemical environment intrinsic to the microbial hosts. We previously reported that a human Fab molecule, referred to as SL335, reactive to human serum albumin has a prolonged in vivo serum half-life in rats. We, herein, tested six discrete SL335-human growth hormone (hGH) fusion constructs as a model system to define an optimal Fab-effector fusion format for E. coli expression. We found that one variant, referred to as HserG/Lser, outperformed the others in terms of a soluble expression yield and functionality in that HserG/Lser has a functional hGH bioactivity and possesses an serum albumin-binding affinity comparable to SL335. Our results clearly demonstrated that the genetic linkage of an effector domain to the C-terminus of Fd (VH + CH1) and the removal of cysteine (Cys) residues responsible for an interchain disulfide bond (IDB) ina Fab molecule optimize the periplasmic expression of a Fab-effector fusion protein in E. coli. We believe that our approach can contribute the development of diverse bi-functional Fab-effector fusion proteins by providing a simple strategy that enables the reliable expression of a functional fusion proteins in E. coli.
<p><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">Ji, S. I., Park, J. H., You, H. G., Chi, H. J., Bang, Y. W., & Cha, S. H. (2019). Intact bioactivities and improved pharmacokinetic of the SL335-IFN-β-1a fusion protein that created by genetic fusion of SL335, a human anti-serum albumin fab, and human interferon-β. </span><em style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">Immunology Letters</em><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">, </span><em style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">207</em><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">, 46-55.</span></p>
Recombinant human interferon beta (rIFN-β) has long been used as a first-line treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS), and any attempt to develop a long-acting rIFN-β is desirable since only one pegylated version of long-acting rIFN-β-1a (Plegridy) is currently available in clinics. Previously, we reported that SL335, a human Fab molecule specific to serum albumin, exhibits an extended serum half-life via utilizing the FcRn recycling mechanism. With the ultimate goal of developing a long-acting rIFN-®, we generated a fusion construct by linking human IFN-β cDNA to the C-terminus of the SL335 H chain at the DNA level followed by expression of the fusion protein, referred to as SL335-IFN-β-1a, in Chinese hamster ovary-S (CHO-S) cells. In its N-linked glycosylated form, the resulting fusion protein was easily purified from the culture supernatant via a three-step chromatography process. In vitro functional assays revealed that the fusion protein retained its intrinsic binding capabilities to human serum albumin (HSA) and interferon α/β receptor (IFNAR) that were almost identical to those of parental SL335 and rIFN-β-1a (Rebif). In addition, the fusion protein possessed an antiviral potency and anti-proliferation activity comparable to those of Rebif. In pharmacokinetic (PK) analyses using Lewis rats and cynomolgus monkeys, SL335-IFN-β-1a exhibited at least a two-fold longer serum half-life and a significantly reduced renal clearance rate compared to those of Rebif. Finally, a four-week repeated dose toxicity study revealed no abnormal toxicological signs. In conclusion, our results clearly demonstrated that SL335-IFN-β-1a is worthy of further development as an alternative long-acting IFN-β therapeutic.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
There are no additional links
Access principles
|
|
Collaborate for developmentConsider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology Not provided |
|
|
Share technical information for match-making assessmentProvide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit Not provided |
|
|
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICsIn the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing Not provided |
Comment & Information
Illustrations
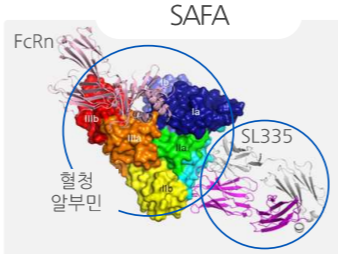
FcRn conjugated with SL335 (API protein)
Investor relations 2014 (no date) AprilBio. Available at: https://file.irgo.co.kr/data/PLAN/ATTACH_PDF/66dce57081c3650b509ae67ee6a245e4.pdf (Accessed: 28 November 2024).
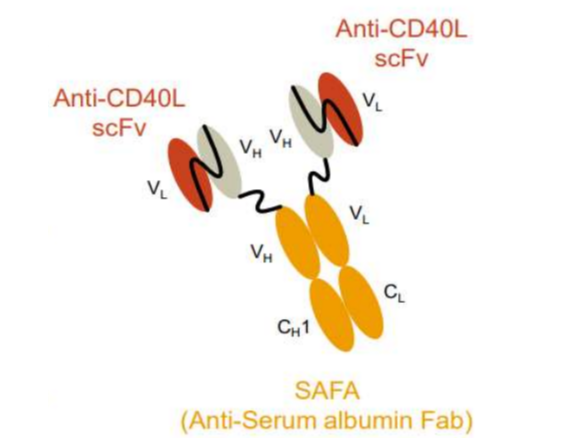
SAFA CD-40L inhibitor (Phase 1 completed)
Investor relations 2014 (no date) AprilBio. Available at: https://file.irgo.co.kr/data/PLAN/ATTACH_PDF/66dce57081c3650b509ae67ee6a245e4.pdf (Accessed: 28 November 2024).
SAFA body conjugated with the serum albumin (protein binding)
AprilBio. (n.d.). AprilBio. AprilBio. Retrieved November 28, 2024, from http://www.aprilbio.com/

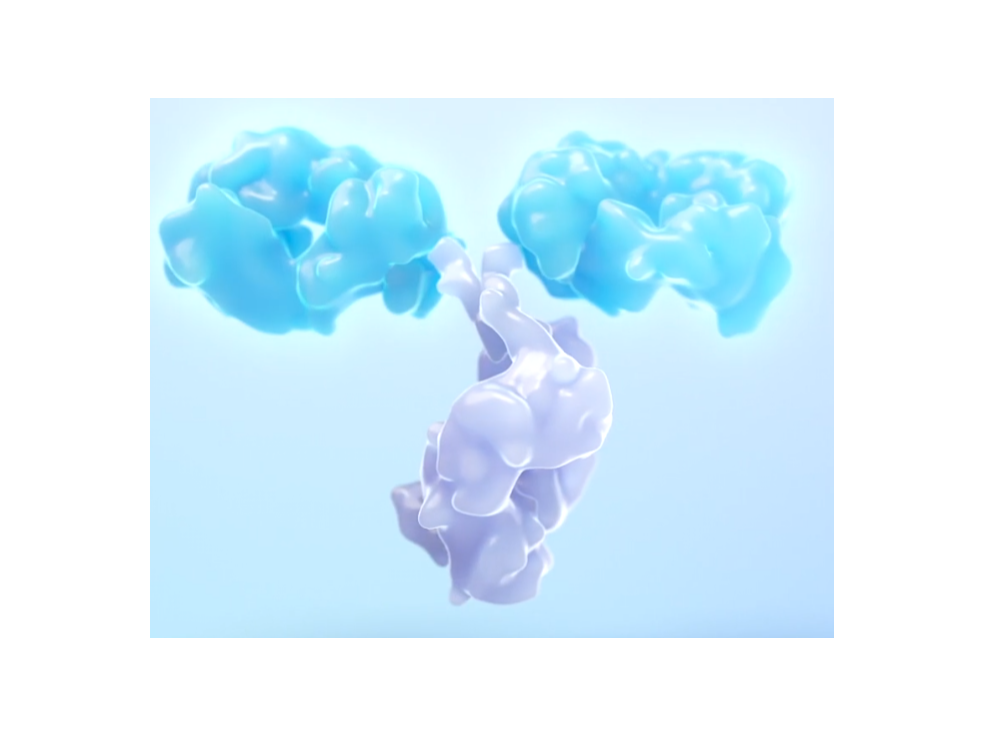
SAFA Body
AprilBio. (n.d.). AprilBio. AprilBio. Retrieved November 28, 2024, from http://www.aprilbio.com/

SAFA Body conjugated with therapeutic proteins
AprilBio. (n.d.). AprilBio. AprilBio. Retrieved November 28, 2024, from http://www.aprilbio.com/