
|
Developed by 

|
Supported by 

|
Ultra-Long-Acting Multi-Purpose In-situ Forming Implant (ISFI)
Verified by the innovator, on Apr 2022Developer(s)

|
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill https://benhabbour.web.unc.edu/US Harnessing engineering, chemistry, and pharmacology tools to design and engineer innovative drug delivery platform technologies for disease treatment and prevention. |
Sponsor(s)

|
NIH-NIAID https://www.niaid.nih.gov/ |
Partnerships
|
No partner indicated |
Technology information
Type of technology
In-situ forming gel/implant
Administration route
Subcutaneous
Development state and regulatory approval
Cabotegravir (CAB), Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA)
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Description
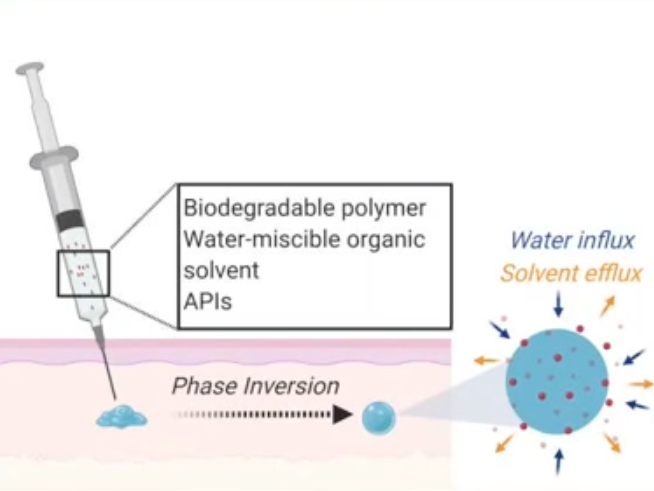
The in-situ forming implant (ISFI) consists of a liquid co-formulation utilizing excipients that form a biodegradable depot after subcutaneous injection for a controlled sustained release of active ingredients. It is based on a biodegradable polymer such as PLGA, a water miscible organic solvent such as NMP and the API or combination APIs of interest.
Technology highlight
First-in-line, ultra-long-acting injectable MPT that offers durable and sustained protection from HIV transmission, high efficacy of contraception, increased user compliance, and the ability to be removed if required. The ISFI offers at least 3 months sustained release after a single subcutaneous administration. It is biodegradable yet removable in case of adverse events or need for treatment reversibility.
Technology main components
poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
Information on the raw materials sourcing, availability and anticipated price
Polymers readily available on the market
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
API desired features
Water-soluble molecules
Water-insoluble molecules
Small molecules
Dolutegravir (DTG), Cabotegravir (CAB), Rilpivirine (RPV)
Nucleic acids
Confidential
Proteins
Confidential
Additional solubility data
Not provided
Additional stability data
Not provided
API loading: Maximum drug quantity to be loaded
To be provided
API co-administration
2 different APIs : at least 2 different APIs
LogP
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Scale-up prospects
To be determined
Tentative equipment list for manufacturing
To be determined
Manufacturing
To be determined
Specific analytical instrument required for characterization of formulation
To be determined
Clinical trials
Not providedExcipients
Proprietary excipients used
No proprietary excipient used
Novel excipients or existing excipients at a concentration above Inactive Ingredients Database (IID) for the specified route of administration
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
Residual solvents used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
Other features of the technology
- Biodegradable
- Drug-eluting
- Monolithic
- Removable
- Single-use
- Room temperature storage
- At least 1 year shelf life
- Needs insertion kit
Release properties
Zero order release
Injectability
26-16 gauge needles
Safety
Absence of adverse local or systemic inflammation when administered to mice or non-human primates
Stability
To be determined
Storage conditions and cold-chain related features
To be determined
Potential application(s)
Therapeutic area(s)
Use case(s)
Use of technology
Ease of administration
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
- To be determined
Frequency of administration
To be determined
User acceptance
To be determined
Targeted user groups
Age Cohort- Adults
- All
- Male
- Female
- Cisgender female
- Cisgender male
- Transgender female
- Transgender male
- Intersex
- Gender non-binary
Pregnant individuals
Yes
Lactating individuals
Yes
Healthy individuals
Unspecified
Comment
Not provided
Potential associated API(s)
Cabotegravir (CAB), Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA)
Class(es)
Not provided
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Cabotegravir (CAB), Etonogestrel (ENG)
Class(es)
Not provided
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Dolutegravir (DTG), Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA)
Class(es)
Not provided
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Dolutegravir (DTG), Etonogestrel (ENG)
Class(es)
Not provided
Development stage
Pre-clinical
Clinical trial number(s)
Not provided
Foreseen/approved indication(s)
Not provided
Foreseen user group
Not provided
Foreseen duration between application(s)
Not provided
Applications to Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRA) / regulatory approvals
Not provided
Patent info
Technology patent families
Patent informations
| Patent description | Representative patent | Categories | Patent holder | Licence with MPP | Patent source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Injectable, biodegradable and removable polymer based drug suspension for ultra-long-acting drug delivery
Expiry date: 2042-06-30 Injectable, biodegradable and removable polymer based drug suspension for ultra-long-acting drug delivery are disclosed. Ultra-long-acting in-situ forming implant (ISFI) drug suspension delivery systems as multipurpose prevention technologies for a multitude of applications are also provided. Methods of use, including treatment of subjects, using the disclosed compositions and ISFIs are also provided. |
WO2023278695 | The University Of North Carolina At Chapel Hill | No | Company |
Patent status
| Patent status/countries | Low, Low- middle and upper-middle | High income |
|---|---|---|
| Granted | ||
| Filed | Albania, North Macedonia, Serbia, Türkiye | Canada, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Cyprus, Czechia, Germany, Denmark, Estonia, Spain, Finland, France, United Kingdom, Greece, Croatia, Hungary, Ireland, Iceland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Latvia, Monaco, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Sweden, Slovenia, Slovakia, San Marino, Japan, United States of America, Bulgaria, Romania |
| Not in force | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) | World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) |
MPP Licence(s)
Supporting material
Publications
<p><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8948873/" rel="noopener noreferrer" target="_blank" style="color: rgb(48, 48, 48);">Effects of Injection Volume and Route of Administration on Dolutegravir In Situ Forming Implant Pharmacokinetics. </a></p><p><br></p><p><span style="color: rgb(48, 48, 48);">Joiner, J. B., King, J. L., Shrivastava, R., Howard, S. A., Cottrell, M. L., Kashuba, A., Dayton, P. A., & Benhabbour, S. R. (2022). </span></p><p><br></p><p><em style="color: rgb(48, 48, 48);"><span class="ql-cursor"></span>Pharmaceutics</em><span style="color: rgb(48, 48, 48);">, </span><em style="color: rgb(48, 48, 48);">14</em><span style="color: rgb(48, 48, 48);">(3), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030615</span></p>
Due to the versatility of the in situ forming implant (ISFI) drug delivery system, it is crucial to understand the effects of formulation parameters for clinical translation. We utilized ultrasound imaging and pharmacokinetics (PK) in mice to understand the impact of administration route, injection volume, and drug loading on ISFI formation, degradation, and drug release in mice. Placebo ISFIs injected subcutaneously (SQ) with smaller volumes (40 μL) exhibited complete degradation within 30–45 days, compared to larger volumes (80 μL), which completely degraded within 45–60 days. However, all dolutegravir (DTG)-loaded ISFIs along the range of injection volumes tested (20–80 μL) were present at 90 days post-injection, suggesting that DTG can prolong ISFI degradation. Ultrasound imaging showed that intramuscular (IM) ISFIs flattened rapidly post administration compared to SQ, which coincides with the earlier Tmax for drug-loaded IM ISFIs. All mice exhibited DTG plasma concentrations above four times the protein-adjusted 90% inhibitory concentration (PA-IC90) throughout the entire 90 days of the study. ISFI release kinetics best fit to zero order or diffusion-controlled models. When total administered dose was held constant, there was no statistical difference in drug exposure regardless of the route of administration or number of injections.
Keywords: long-acting, in situ, injectable, biodegradable, implants, PLGA, controlled release, drug delivery, ultrasound, pharmacokinetics
<p><a href="https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/13/15/2450/htm" rel="noopener noreferrer" target="_blank" style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">Multipurpose Prevention Technologies: Oral, Parenteral, and Vaginal Dosage Forms for Prevention of HIV/STIs and Unplanned Pregnancy. </a></p><p><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">Young IC, Benhabbour SR. </span></p><p><em style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);"><span class="ql-cursor"></span>Polymers</em><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34);">. 2021; 13(15):2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152450</span></p>
There is a high global prevalence of HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and unplanned pregnancies. Current preventative daily oral dosing regimens can be ineffective due to low patient adherence. Sustained release delivery systems in conjunction with multipurpose prevention technologies (MPTs) can reduce high rates of HIV/STIs and unplanned pregnancies in an all-in-one efficacious, acceptable, and easily accessible technology to allow for prolonged release of antivirals and contraceptives. The concept and development of MPTs have greatly progressed over the past decade and demonstrate efficacious technologies that are user-accepted with potentially high adherence. This review gives a comprehensive overview of the latest oral, parenteral, and vaginally delivered MPTs in development as well as drug delivery formulations with the potential to advance as an MPT, and implementation studies regarding MPT user acceptability and adherence. Furthermore, there is a focus on MPT intravaginal rings emphasizing injection molding and hot-melt extrusion manufacturing limitations and emerging fabrication advancements. Lastly, formulation development considerations and limitations are discussed, such as nonhormonal contraceptive considerations, challenges with achieving a stable coformulation of multiple drugs, achieving sustained and controlled drug release, limiting drug–drug interactions, and advancing past preclinical development stages. Despite the challenges in the MPT landscape, these technologies demonstrate the potential to bridge gaps in preventative sexual and reproductive health care.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Access principles
|
|
Collaborate for developmentConsider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology Not provided |
|
|
Share technical information for match-making assessmentProvide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit Not provided |
|
|
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICsIn the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing Not provided |
Comment & Information
Illustrations

ISFI mechanism and drug release. A liquid solution incorporating a biodegradable polymer, water-miscible organic solvent, and APIs is subcutaneously administered and undergoes a phase inversion
Young I, Benhabbour SR et al. CROI, 2022
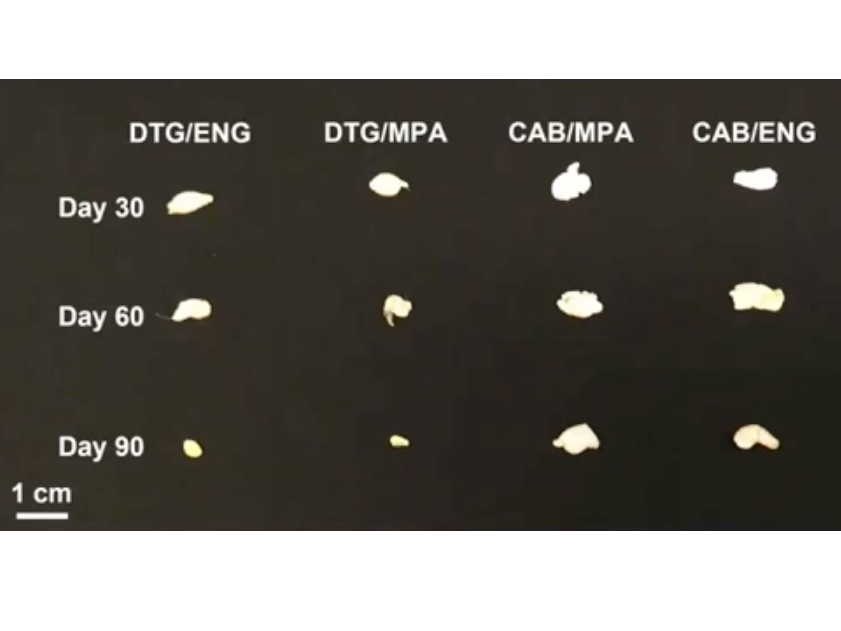
Depots retrieved 90 days post subcutaneous administration in mice model to quantify residual drug and polymer degradation
Young I, Benhabbour SR et al. CROI 2022