Type of technology
Peptides and peptide-like molecules, In-situ forming gel/implant
Administration route
Subcutaneous, Intramuscular, Intra-vitreal
Development state and regulatory approval
Anti-infectives for systemic use, Antivirals for systemic use, Cabotegravir (CAB), Lamivudine (3TC)
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Description
We have created a soluble injection that is able to incorporate multiple drugs in a water-based solvent. This forms a hydrogel implant in response to enzymes present within the skin to release drugs long-term, removing the need for daily dosing. Our injectable implant is composed of peptide-like molecules which are capable of forming tissue-like hydrogels that can be tailored to gradually release drugs. This will remove the need for patients to comply with complex drug dosing regimens on a daily basis and improve their adherence to medication
Developer(s)

Queen's University Belfast is a leading UK university for knowledge exchange, and commercialisation. The School of Pharmacy is one of Queen's University Belfast's most prestigious departments and a global leader in drug delivery. It is the top ranking UK School of Pharmacy (Complete University Guide 2024) and 39th in the world (2023 QS Rankings).
Technology highlight
We have so far proven our technology can deliver the HIV drug zidovudine to rats at IC90 values for at least 35 days. We believe protection can be lengthened i.e. to 84 days by using more potent HIV antiretrovirals and are currently working on this goal. These results formed part of a recent publication in Advanced Healthcare Materials (2023). DOI: doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202203198. We have also demonstrated hydrogel formation and sustained release using several drugs/diseases (doxorubicin [cancer], haloperidol [antipsychotic]) and as a single injectable multipurpose technology (HIV prevention + contraception). Our most promising technology has formed part of a patent submission to the UK Patent Office on 31st March 2023 (2304871.3).
Illustration(s)
Technology main components
Low molecular weight peptide and peptide-mimetic (peptoid, D-peptide) molecules covalently attached to drugs.
Fmoc protected amino acids, primary amines
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
This formulation works best with drugs of low molecular weight (<~1200 Da) as it allows precise covalent attachment of drug to the peptide/peptide-like molecule. There is the potential to study delivery of larger biologics but these would likely have to be physically mixed with peptide/peptide-like molecule.
Not provided
Not provided
We have tested up to 5%w/v so far. We see no reason why this could not be increased as the peptide provides increased water solubility to drugs.
3 different APIs : We have tested up to 3 hydrophobic drugs successfully so far (2xHIV antiretrovirals + 1 contraceptive hormone)
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
The formulation's peptide/peptide-like molecule is low molecular weight and can be readily synthesised using common solid phase synthesis protocols. The impact of manufacture on synthetic factors should be considered e.g. yield, raw material availability, novel vs. established methods of chemical conjugation, chemical orthogonality, analysing to regulatory requirements e.g. Pharmacopoeial, green chemistry and overall cost.
Preparative LC with Mass Spec capability for efficient purification
The peptide is made by chemical synthesis, requirements will depend mainly of drug of interest. e.g. a steroid drug for contraception will required increased safety considerations in line with cGMP.
Analytical HPLC, preferably with Mass Spec capability. Hydrogen and Phosphate NMR.
Excipients
No proprietary excipient used
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
Not provided
Additional features
- Biodegradable
- Single-use
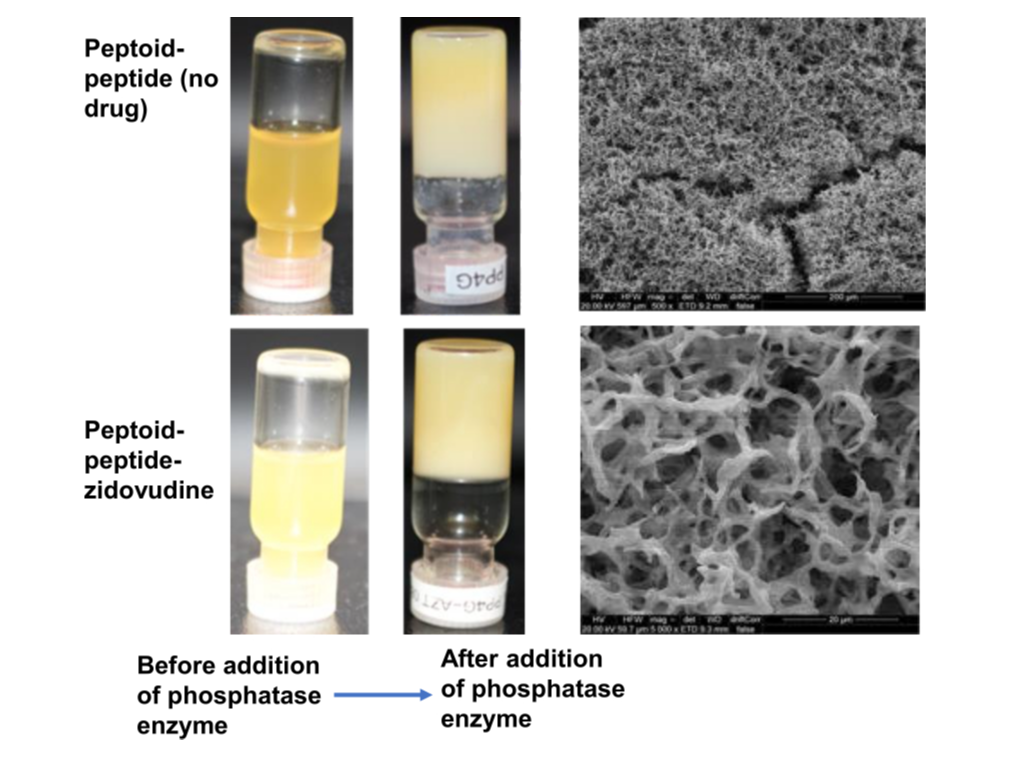
Zidovudine drug burst release reduced by 30% (from 79% released at 72 hrs, physical encapsulation) to 48% release upon attachment of drug to our most promising molecule a peptoid-peptide.
Injected as a solution, rapidly forms a hydrogel upon administration. Hydrogel begins to form within 1-2 minutes, fully forms ~20 minutes. The low viscosity and volume of the dissolved formulations permit use of narrow bore needles to improve patient acceptance.
No signifiicant toxicity (L929 cells) via Live/Dead, MTS and LDH assays. Studies in rats (histological, mass) show no adverse effects for study period (at least 2 months currently).
Currently undergoing ICH stability assays. Type 1 glass vials preferred packaging choice as they offer the highest hydrolytic resistance.
In practice, this formulation – prepared as highly stable freeze-dried powders – will be first readily dissolved in sterile water/buffer and then immediately administered via injection.
Therapeutic area(s)
- Malaria
- Contraception
- Multipurpose technology : "Combined HIV prevention and contraception in one injectable product"
- HIV
- Oncology
- Substance use disorders
- Mental health
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
- Treatment
Potential associated API(s)
- Anti-infectives for systemic use , Antivirals for systemic use , Cabotegravir (CAB) , Lamivudine (3TC)
- Genito-urinary system and sex hormones , Progestogens
- Haloperidol
- Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
Use of technology
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
- Self-administered
Monthly, We are aiming for a minimum dosgae interval of every 3 months (84 days)
We have performed studies with UK HIV charity Positive Life NI. Patients demonstrate a high interest in the use of such technology to replace oral medicines.
Targeted user groups
- Adolescents
- Adults
- All
Unspecified
Unspecified
Unspecified
Main target group would be within adolescent and young women who require a discrete technology to provide combined HIV prevention and contraception.
Anti-infectives for systemic use , Antivirals for systemic use , Cabotegravir (CAB) , Lamivudine (3TC)
antiviral
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV prevention
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Genito-urinary system and sex hormones , Progestogens
Contraceptive
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Combined HIV prevention and contraception
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Haloperidol
Not provided
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
Anthracycline chemotherapy
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Cancer
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Patent application submitted to UK Patent Office on 31st March 2023. • United Kingdom Priority Patent Application No. 2304871.3 AN INJECTABLE DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR LONG-ACTING ADMINISTRATION OF DRUGS "Peptoid-peptide hydrogel drug delivery platform" filed 31/03/2023.
Not provided
Patent Application No. 2304871.3
Formulation/platform
Garry Laverty, Sreekanth Pentlavalli, Sophie Coulter, Emily Cross, Queen's University Belfast
Not provided
Not provided
Applied awaiting approval
Publications
Eradicating HIV/AIDS by 2030 is a central goal of the World Health Organization. Patient adherence to complicated dosage regimens remains a key barrier. There is a need for convenient long-acting formulations that deliver drugs over sustained periods. This paper presents an alternative platform, an injectable in situ forming hydrogel implant to deliver a model antiretroviral drug (zidovudine [AZT]) over 28 days. The formulation is a self-assembling ultrashort d or l-α peptide hydrogelator, namely phosphorylated (naphthalene-2-ly)-acetyl-diphenylalanine-lysine-tyrosine-OH (NapFFKY[p]-OH), covalently conjugated to zidovudine via an ester linkage. Rheological analysis demonstrates phosphatase enzyme instructed self-assembly, with hydrogels forming within minutes. Small angle neutron scattering data suggest hydrogels form narrow radius (≈2 nm), large length fibers closely fitting the flexible cylinder elliptical model. d-Peptides are particularly promising for long-acting delivery, displaying protease resistance for 28 days. Drug release, via hydrolysis of the ester linkage, progress under physiological conditions (37 °C, pH 7.4, H2O). Subcutaneous administration of Napffk(AZT)Y[p]G-OH in Sprague Dawley rats demonstrate zidovudine blood plasma concentrations within the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) range (30–130 ng mL−1) for 35 days. This work is a proof-of-concept for the development of a long-acting combined injectable in situ forming peptide hydrogel implant. These products are imperative given their potential impact on society.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
There are no additional links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing