Type of technology
Aqueous drug particle suspension
Administration route
Intramuscular, Subcutaneous
Development state and regulatory approval
Cabotegravir (CAB)
Pre-clinical
XVIR-110 (Cabotegravir 18 Carbon ester prodrug) is prepared for IND
Description
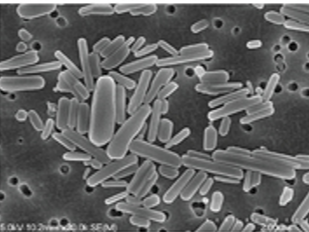
ProTide Prodrug Technology is an ultra-long-acting nanoformulation. The Pro-Tide technology contains nanocrystals of ester prodrug of the API. Further, the duration of the formulation is dependent on the carbon length of the ester fatty acid. In addition to that, the lipophilicity of the prodrug depends on the physiochemical properties of the fatty acid and the location of the fatty acid attached. Also, this nanoformulation has no residual solvents.
Developer(s)

Exavir Therapeutics is a spun-out company that originated in 2020 by Alborz and was developed by the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Exavir is specialized in ultra-long-acting drug delivery systems. Exavir has received an NIAD grant in 2023. Exavir currently works on HIV therapeutics off-patent drugs. Howard Gendelman and other researchers play a vital role in Exavir.
Technology highlight
1) ProTide prodrugs have controlled hydrolysis of the ester chain. The length of the carbon chain can be customizable based on the API. 2) Tissue penetrance can be overcome. 3) Prolonged drug release, plasma circulation rate, and tissue binding of API. 4) Poloxamer 407 is used as a stabilizer; thus, the formulation is stable for 98 days in vivo.
Illustration(s)
Technology main components
1) ProTide prodrug (14 to 18 carbon ester-linked API) 2) Poloxamer 308 and/or 407 3) Other excipients such as surfactants.
Not provided
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
The ProTide formulation targets non-nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors and integrase strand transfer inhibitors such as cabotegravir, tenofovir, dolutegravir, and nevirapine.
The solubility of each ProTide can be tailored by modifying the physicochemical properties of the API through adjustments to the hydrophilic or hydrophobic nature of the ester chain, specifically by varying the length of the fatty acid moiety.
Not provided
75-90 wt%
1 single API :
Min: -1.6 Max: 4
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
The Exavir does not have its own manufacturing facilities.
Avestin EmulsiFlex-C3 High-pressure homogenizer
1. Disperse solid drug/prodrug in a poloxamer 407 solution at a drug/prodrug to surfactant ratio of 10:1 w/w in endotoxin-free water to form a presuspension. 2. Homogenize the presuspension using an Avestin EmulsiFlex-C3 high-pressure homogenizer at 20,000 ± 1000 PSI until the desired particle size is achieved. 3. Characterize formulations for particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential using DLS with a Malvern Zetasizer Nano-ZSP. 4. Quantify drug loading using LC-MS. 5. Assess endotoxin concentrations using a Charles River Endosafe Nexgen system.
1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) 2. Dynamic Light Scattering + Malvern Zetasizer Nano-ZSP 3. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) 4. Charles River Endosafe Nexgen system
Excipients
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Additional features
- At least 1 year shelf life
Nanocrystals facilitate drug delivery to macrophages by forming intracellular and tissue drug reservoirs within endosomes. This intracellular sequestration shields the drug from systemic circulation, thereby extending the half-life of the API. The prodrug undergoes biotransformation into its active form through intracellular kinase-mediated activation.
ProTide formulations are injected via intramuscular injection via a 20-25 gauge needle.
No safety concerns were observed in the preclinical toxicology studies. Further, clinical safety studies are yet to be conducted.
In preclinical stability studies of the CAB 18-carbon ester ProTide prodrug nanoparticles, the prodrug demonstrated approximately 100% stability, with negligible drug release observed from the intact nanoparticles over the course of one year of storage.
Studies show that the formulation can maintain its integrity over 98 days under various storage conditions.
Therapeutic area(s)
- Other(s) : "Opoid Use Disorder"
- HIV
Not provided
Potential associated API(s)
- Cabotegravir (CAB)
- Dolutegravir (DTG)
- Tenofovir (TFV)
- Rilpivirine (RPV)
- Bictegravir (BIC)
Use of technology
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
Once every 6 months, Yearly
Not provided
Targeted user groups
- Adults
- Older Adults
- Male
- Female
Unspecified
Unspecified
Unspecified
Not provided
Cabotegravir (CAB)
HIV integrase strand transfer inhibitor
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV Treatment and PrEP
Not provided
Once yearly
XVIR-110 (Cabotegravir 18 Carbon ester prodrug) is prepared for IND
Dolutegravir (DTG)
HIV integrase inhibitors
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV treatment and PrEP
Not provided
Once yearly
Not provided
Tenofovir (TFV)
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV Treatment and PrEP
Not provided
Once yearly
Not provided
Rilpivirine (RPV)
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV Treatment and PrEP
Not provided
Once yearly
Not provided
HIV integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV Treatment and PrEP
Not provided
Six monthly
Not provided
Antiviral prodrugs compounds and crystalline nanoparticle formulations
Prodrug compounds of cabotegravir (CAB), raltegravir (RAL), elvitegravir (EVG), dolutegravir (DTG), bictegravir (BIC), BI 224436, and MK-2048. Crystalline nanoparticle formulations comprising one of the prodrugs listed above and and at least one polymer or surfactant. Method of use of said formulation for treating HIV
WO2020086555
Compound/Formulation/Method of treatment
Board of regents of the University of Nebraska
Not provided
October 22, 2039
Granted: CN, US, MX, EP (BE, CH, CY, DE, ES, FI, FR, GB, HU, IE, IT, LI, LU, MC, MT, NL, RO), SA, EA (AM, AZ, BY, KG, KZ, RU, TJ, TM), Pending: AU, BR, CA, EG, HK, ID, IL, JP, KR, MY, NZ, PH, SG Not in force: AT, BG, CZ, DK, EE, GR, HR, IS, LT, LV, NO, PT, RS, SE, SI, SK, SM, TR, IN, , KH, MA, MD, TN, BA, ME
Publications
Kulkarni, T. A., Bade, A. N., Sillman, B., Shetty, B. L. D., Wojtkiewicz, M. S., Gautam, N., Hilaire, J. R., Sravanam, S., Szlachetka, A., Lamberty, B. G., Morsey, B. M., Fox, H. S., Alnouti, Y., McMillan, J. M., Mosley, R. L., Meza, J., Domanico, P. L., Yue, T. Y., Moore, G., Edagwa, B. J., … Gendelman, H. E. (2020). A year-long extended release nanoformulated cabotegravir prodrug. Nature materials, 19(8), 910–920. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0674-z
Long-acting cabotegravir (CAB) extends antiretroviral drug administration from daily to monthly. However, dosing volumes, injection site reactions and health-care oversight are obstacles towards a broad usage. The creation of poloxamer-coated hydrophobic and lipophilic CAB prodrugs with controlled hydrolysis and tissue penetrance can overcome these obstacles. To such ends, fatty acid ester CAB nanocrystal prodrugs with 14, 18, and 22 added carbon chains were encased in biocompatible surfactants named NMCAB, NM2CAB, and NM3CAB and tested for drug release, activation, cytotoxicity, antiretroviral activities, pharmacokinetics, and biodistribution. Pharmacokinetics studies, performed in mice and rhesus macaques with the lead 18-carbon ester chain NM2CAB, showed plasma CAB levels above the protein-adjusted 90% inhibitory concentration for up to a year. NM2CAB, compared with NMCAB and NM3CAB, demonstrated a prolonged drug release, plasma circulation time and tissue drug concentrations after a single 45 mg per kg body weight intramuscular injection. These prodrug modifications could substantially improve CAB's effectiveness.
Cobb, D. A., Smith, N., Deodhar, S., Bade, A. N., Gautam, N., Shetty, B. L. D., McMillan, J., Alnouti, Y., Cohen, S. M., Gendelman, H. E., & Edagwa, B. (2021). Transformation of tenofovir into stable ProTide nanocrystals with long-acting pharmacokinetic profiles. Nature communications, 12(1), 5458. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25690-5
Treatment and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus type one (HIV-1) infection was transformed through widespread use of antiretroviral therapy (ART). However, ART has limitations in requiring life-long daily adherence. Such limitations have led to the creation of long-acting (LA) ART. While nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI) remain the ART backbone, to the best of our knowledge, none have been converted into LA agents. To these ends, we transformed tenofovir (TFV) into LA surfactant stabilized aqueous prodrug nanocrystals (referred to as NM1TFV and NM2TFV), enhancing intracellular drug uptake and retention. A single intramuscular injection of NM1TFV, NM2TFV, or a nanoformulated tenofovir alafenamide (NTAF) at 75 mg/kg TFV equivalents to Sprague Dawley rats sustains active TFV-diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels ≥ four times the 90% effective dose for two months. NM1TFV, NM2TFV and NTAF elicit TFV-DP levels of 11,276, 1,651, and 397 fmol/g in rectal tissue, respectively. These results are a significant step towards a LA TFV ProTide.
Deodhar, S., Sillman, B., Bade, A. N., Avedissian, S. N., Podany, A. T., McMillan, J. M., Gautam, N., Hanson, B., Dyavar Shetty, B. L., Szlachetka, A., Johnston, M., Thurman, M., Munt, D. J., Dash, A. K., Markovic, M., Dahan, A., Alnouti, Y., Yazdi, A., Kevadiya, B. D., Byrareddy, S. N., … Gendelman, H. E. (2022). Transformation of dolutegravir into an ultra-long-acting parenteral prodrug formulation. Nature communications, 13(1), 3226. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30902-7
Ultra-long-acting integrase strand transfer inhibitors were created by screening a library of monomeric and dimeric dolutegravir (DTG) prodrug nanoformulations. This led to an 18-carbon chain modified ester prodrug nanocrystal (coined NM2DTG) with the potential to sustain yearly dosing. Here, we show that the physiochemical and pharmacokinetic (PK) formulation properties facilitate slow drug release from tissue macrophage depot stores at the muscle injection site and adjacent lymphoid tissues following single parenteral injection. Significant plasma drug levels are recorded up to a year following injection. Tissue sites for prodrug hydrolysis are dependent on nanocrystal dissolution and prodrug release, drug-depot volume, perfusion, and cell-tissue pH. Each affect an extended NM2DTG apparent half-life recorded by PK parameters. The NM2DTG product can impact therapeutic adherence, tolerability, and access of a widely used integrase inhibitor in both resource limited and rich settings to reduce HIV-1 transmission and achieve optimal treatment outcomes.
Cobb, D. A., Smith, N., Deodhar, S., Bade, A. N., Gautam, N., Shetty, B. L. D., McMillan, J., Alnouti, Y., Cohen, S. M., Gendelman, H. E., & Edagwa, B. (2021). Transformation of tenofovir into stable ProTide nanocrystals with long-acting pharmacokinetic profiles. Nature communications, 12(1), 5458. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25690-5
Treatment and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus type one (HIV-1) infection was transformed through widespread use of antiretroviral therapy (ART). However, ART has limitations in requiring life-long daily adherence. Such limitations have led to the creation of long-acting (LA) ART. While nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI) remain the ART backbone, to the best of our knowledge, none have been converted into LA agents. To these ends, we transformed tenofovir (TFV) into LA surfactant stabilized aqueous prodrug nanocrystals (referred to as NM1TFV and NM2TFV), enhancing intracellular drug uptake and retention. A single intramuscular injection of NM1TFV, NM2TFV, or a nanoformulated tenofovir alafenamide (NTAF) at 75 mg/kg TFV equivalents to Sprague Dawley rats sustains active TFV-diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels ≥ four times the 90% effective dose for two months. NM1TFV, NM2TFV and NTAF elicit TFV-DP levels of 11,276, 1,651, and 397 fmol/g in rectal tissue, respectively. These results are a significant step towards a LA TFV ProTide.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
There are no additional links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing
Partnerships
No partner indicated