Technology name
Dissolving microarray patches
Developer(s)
Type of technology
Polymer-based particles, In-situ forming gel/implant, Aqueous drug particle suspension, Transdermal patch
Administration route
Intradermal delivery of long-acting drug formulations
Development state and regulatory approval
Cabotegravir (CAB)
Pre-clinical
N/A
Description
Biocompatible polymeric microneedle system that painlessly and without drawing blood penetrates the skin's stratum corneum barrier and then dissolves to deposit long-acting drug formulations in the viable skin layers. This technology could be a replacement for long-acting intramuscular injections
Developer(s)

Queen's University Belfast
Currently focusing on research in the field of microneedles/microarray patches, minimally-invasive patient monitoring/diagnosis, transdermal drug delivery, including biomolecules, vaccine delivery, photodynamic therapy, nanomedicine delivery, HIV treatment and prevention, delivery of therapeutics for tropical diseases and rare conditions.
Technology highlight
Avoids needle stick injuries, no cold chain required, high-dose delivery system, easy to use by patients at home, self-disabling system, with specialist disposal not required
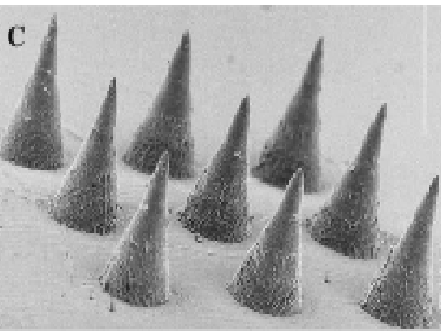
Illustration(s)
Technology main components
Microneedles composed of FDA-approved biocompatible polymers
PVA and PVP, the typical dissolving polymers, are inexpensive and can readily be obtained by pharmaceutical excipient manufacturers. Sometimes, PLGA will be required to sustain release of more water soluble molecules. PLGA is more expensive, but Ashland and Evonik offer many different products with controllable biodegradation properties that are suitable for injectable products.
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
Unit: mg/mL
Microneedles are suitable for a wide range of therapeutic classes. Formulation can be readily adjusted as required
Unit: mg/mL
Both soluble (e.g. tenofovir alafenamide fumarate) and poorly soluble (e.g. rilpivirine, cabotegravir) can be delivered. Formulations can be adjusted as needed to obtain the delivery rate desired
Rilpivirine, cabotegravir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, etravirine
DNA and RNA vaccines
Therapeutic antibodies and single domain antibodies, protein vaccines and peptides (e.g. insulin, exenatide)
N/A
N/A
75-90 wt%
2 different APIs : At least two
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Microneedle products can now be made at scale by a number of manufacturers to GMP conditions - For example, by LTS Lohmann - https://ltslohmann.de/en/micro-array-patches/
Confidential. Each manufacturer is unlikely to disclose such details without a CDA
It is likely a low bioburden product will be required
HPLC-MS, XRD, DSC, TGA, FT-IR, texture profile analysis, optical coherence tomography
Excipients
PVA, PVP and, when needed, PLGA
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
- Drug-eluting
- At least 1 year shelf life
Sustained release enabled by the drug formulation - the microneedles act as a tool to place the long-acting system in the viable skin layers
Applied to the skin and the needles penetrate the stratum corneum, then dissolve and deposit the long-acting drug formulation in the viable skin layers
No needle stick injuries. no specialised disposal required, as the microneedles dissolve in skin
Not provided
No cold chain needed, as the system is dry-state and so very stable
Therapeutic area(s)
- HIV
- Disease agnostic
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
- Treatment
Potential associated API(s)
- Rilpivirine (RPV)
- Cabotegravir (CAB)
- Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)
Use of technology
- Self-administered
Weekly, Monthly
Many studies have been conducted in this area - Freely available in the literature
Targeted user groups
- Children
- Adolescents
- Adults
- Older Adults
- Neonates
- All
Unspecified
Unspecified
Unspecified
People in their own homes, including children
Rilpivirine (RPV)
anti-retroviral
Pre-clinical
N/A
HIV prevention and treatment
HIV patients and PreP patients
1 week to 1 month
N/A
Cabotegravir (CAB)
anti-retroviral
Pre-clinical
N/A
HIV treatment and prevention
HIV patients and PreP patients
1 week to 1 month
N/A
Antiviral (NRTI)
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
There are either no relevant patents or these were not yet submitted to LAPaL
Publications
There are no publication
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing

