Technology name
Last update: Sep 2025Cloudbreak (r)
Developer(s)
Sponsor(s)
Not specified
Type of technology
Peptide of Human Antibody Fragment (Fc) coupled with drug molecule, Monoclonal antibodies and antibody drug conjugates
Administration route
Subcutaneous, Intramuscular, Intravenous
Development state and regulatory approval
Temsavir
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Description
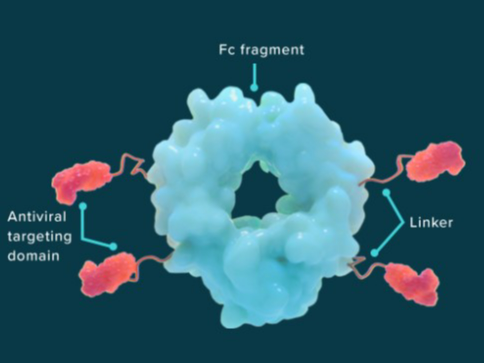
Cloudbreak (r) is a Drug Fc Conjugate that acts as a single-molecule cocktail by coupling targeted small molecules and peptides to a human antibody fragment (Fc). These conjugates bind to the target receptors for an extended period while simultaneously engaging with the immune system of the human body, allowing them to both treat and prevent disease. antibody drug conjugates like this have the potential to carry multiple drug molecules (payloads).
Developer(s)

Cidara Therapeutics
Cidara Therapeutics has developed a drug development pipeline platform called CloudBreak which is based on API conjugation with antibody fragment conjugate. This Drug Fc conjugate is a targeted immunotherapy that inhibits specific disease targets while simultaneously engaging the immune system. Cidara's portfolio includes novel therapeutics targeting viral infections and solid tumors.
Technology highlight
• Long half-life, similar to monoclonal antibody • Ability to target cryptic sites & has small molecule binding pockets • Targeted pharmacological action with low systematic exposure • Multivalent target engagement of DFC increases potency of API and reduces resistance potential • Extracellular targeted action
Illustration(s)
Technology main components
Drug -Fc Conjugate cocktail consists of (i) API, (ii) peptide fusions, and (iii) a human antibody fragment specific to the targeted disease (Fc MOIETY).
Not provided
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
The DFC technology targets small molecules like Influenza neuroaminidase inhibitors (such as oseltamivir, zanamivir, peramivir, and laninamivir), CD73 inhibitors, CCR antagonists and GP120 inhibitors (such as temsavir).
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
WuXi XDC partnered with Cidara Therapeutics to manufacture DFC formulations. WuXi recently established a new manufacturing facility with the capacity to produce 200-2000 litres of DFC formulation per batch.
Not provided
Manufacturing of DFC formulation has low COGS.
HPLC analytical procedure is used for the gross content and assay of reconstituted solution tests in the drug product specification
Excipients
No proprietary excipient used
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
- Drug-eluting
- Other(s)
Targeted action
Small molecule conjugates in DFC exhibit selective targeting towards enzyme active sites and receptors. The distribution of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is influenced by the molecular size of the DFC, with smaller sizes facilitating faster tissue penetration. The API is released from the Fc domain at the target site in a cumulative manner, optimizing therapeutic efficacy through sustained and controlled delivery for a longer period of time.
Preclinical and clinical studies focused on DFC drug candidates administered via intramuscular (IM) and subcutaneous (SQ) routes. For administration, a 25-gauge or larger bore needle is used.
Interim analysis of Phase 2a studies of CD-388 shows that the drug was well-tolerated with no treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) or serious adverse events (SAE) in 28 subjects who received CD-388.
Not provided
The formulation should be stored at 20°C–25°C. It can also be stored at 5°C–25°C for up to 24 hours.
Therapeutic area(s)
- Other(s) : "Influenza A & C infection"
- Oncology
- HIV
- Treatment
Potential associated API(s)
- Temsavir
- zanamivir
Use of technology
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
Weekly, Single dose administration
Not provided
Targeted user groups
- Adults
- Older Adults
- All
No
No
Unspecified
Not provided
Temsavir
Antiretroviral
Pre-clinical
Not provided
HIV
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
zanamivir
antiviral (neuraminidase inhibitor)
Phase II
NCT06609460
Seasonal influenza
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Compositions and methods for the treatment of viral infections include conjugates containing inhibitors of viral neuraminidase and MoT influenza or parainfluenza
Compositions and methods for the treatment of viral infections include conjugates containing inhibitors of viral neuraminidase (e.g., zanamivir, peramivir, or analogs thereof) linked to an Fc monomer, an Fc domain, and Fc-binding peptide, an albumin protein, or albumin-binding peptide. In particular, conjugates can be used in the treatment of viral infections (e.g., influenza viral infections).
WO2021046549
Compound, Composition
Cidara Therapeutics, Inc
Not provided
September 8, 2040
Granted: ZA, US, CO, AU, JP, NZ, CN Pending: HK, AE, BR, CA, CL, CR, EA, EC, EP (LMICs: AL, MK, TR, BA, ME, KH, MA, MD, TN, RS), ID, IL, KR, MX, MY, PE, PH, SA, SG, TH, TW, UA, VN, IN Withdrawn: ARIPO
Conjugates of inhibitors of viral gp120 receptor (e.g., temsavir or analogs thereof) linked to an Fc monomer, an Fc domain, and Fc-binding peptide and use for treating HIV
Conjugates containing viral gp120 receptor inhibitors (e.g., temsavir, BMS-818251, DMJ-ll-121, BNM-IV-147, or analogues thereof) linked to an Fc monomer, an Fc domain, an Fc-binding peptide, an albumin protein, or an albumin-binding peptide are used in the treatment of viral infections. These conjugates are particularly useful in the treatment of HIV infections.
WO2020252393
Compound
Cidara Therapeutics, Inc
Not provided
June 12, 2040
Pending: AU, CA, CN, JP, US Not in force: EP
Variant Fc domain monomer with linked to cyclic heptapeptides and method for treatment of bacterial infection
Conjugates with an Fc domain covalently bonded to one or more monomers or dimers of cyclic heptapeptides are among the compositions and methods used to treat bacterial infections. These small-molecule conjugates have the potential to treat gram-negative bacterial infections.
WO2018128826
Compound
Cidara Therapeutics, Inc
Not provided
December 20, 2037
Filed and pending in US only
Publications
There are no publication
Additional documents
Useful links
There are no additional links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing
