Technology name
Scalable process to achieve LA injectable delivery of insoluble medicines
Sponsor(s)
Type of technology
Aqueous drug particle suspension
Administration route
Subcutaneous, Intramuscular
Development state and regulatory approval
Niclosamide
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Description
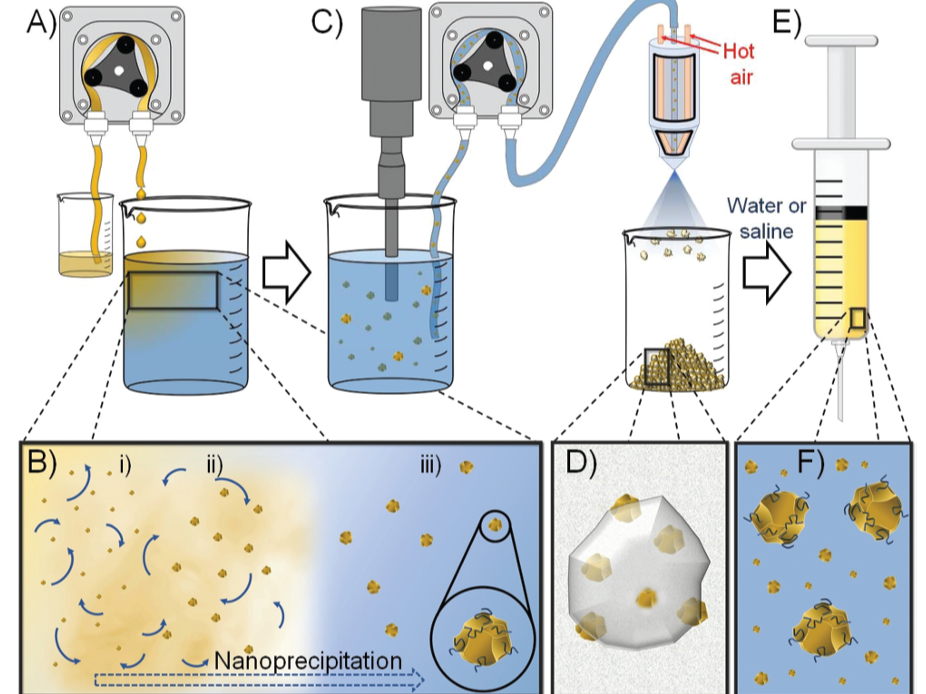
Nanoprecipitation technology to form redispersible solid drug nanoparticles (SDN) formulations that may be stored as solids, reconstituted with water and utilised as long-acting injectables to provide extended drug exposure, of otherwise highly insoluble drugs.
Developer(s)
The team is a multidisciplinary collaboration of materials chemists and pharmacologists. Their research focuses on developing and delivering new LA technologies and candidate LA therapeutics for a range of diseases. Also, the team is driving the conversation around LA opportunities to encourage uptake and build awareness
Technology highlight
This technology broadens the use of a highly insoluble drug molecule and generates high injectable concentrations of particles in an aqueous medium and to achieve extended release of medicines. The drug has very low bioavailability but IM injection leads to prolonged plasma exposure
Illustration(s)
Technology main components
Polymer (eg. hydroxypropyl methylcellulose), Surfactant (eg. Tween 20, Pluronic (r) F127), Sugar (eg. sucrose) Nanoprecipitation into water from Class3 solvents
readily available and low-price materials - selected from the FDA CDER list of Inactive Ingredients
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
APIs compatibility profile
Niclosamide, nitazoxanide, atovaquone
Not provided
Not provided
50-75 wt%
1 single API :
Not provided
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
The process is highly scalable
spray-dryer
Not provided
dynamic light scattering (eg. Malvern Panalytical ZetaSizer Ultra Proton Correlation Spectroscope)
Excipients
No proprietary excipient used
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
No residual solvent used
Additional features
- Biodegradable
- Non-removable
- Room temperature storage
- At least 1 year shelf life
Extended drug exposure for > 1 month from single administration
injectable (IM or SC) - reconstitutable solid at the point of need
No safety issues identified during preclinical work
Drug substance is stable to terminal sterilisation by irradiation
No cold chain requirement
Therapeutic area(s)
- COVID 19
- Other(s) : "Niclosamide has numerous claimed effects, including influenza, oncology, and antibacterial benefits"
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
- Treatment
Potential associated API(s)
Use of technology
- Administered by a community health worker
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
Monthly
Not provided
Targeted user groups
- Adults
- All
Unspecified
Unspecified
Unspecified
Not provided
antiparasitic
Pre-clinical
Not provided
Prophylaxis and7or therapy of SARS-CoV2
Not provided
1 month
Not provided
The present invention relates to solid compositions of pharmaceutically active compounds, aqueous dispersions derived from these compositions and processes for the preparation of these solid compositions and dispersions. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions derived from these solid compositions and dispersions, and their use in the treatment and/or prophylaxis of helminthic, protozoal, and viral infections.
Not provided
WO2022101623 (A1)
Process
University of Liverpool
No exclusivity or licence in place
May 14, 2034
Filed
Publications
Hobson JJ , Savage AC , Dwyer AB , Unsworth C , Massam J , Arshad U , Pertinez H , Box H , Tatham L , Rajoli RKR , Neary M , Sharp J , Valentijn A , David C , Curley P , Liptrott NJ , McDonald TO , Owen A , Rannard SP . Scalable nanoprecipitation of niclosamide and in vivo demonstration of long-acting delivery after intramuscular injection. Nanoscale. 2021 Apr 7;13(13):6410-6416. doi: 10.1039/d1nr00309g. Epub 2021 Mar 25. PMID: 33885522.
The control of COVID-19 across the world requires the formation of a range of interventions including vaccines to elicit an immune response and immunomodulatory or antiviral therapeutics. Here, we demonstrate the nanoparticle formulation of a highly insoluble drug compound, niclosamide, with known anti SARS-CoV-2 activity as a cheap and scalable long-acting injectable antiviral candidate.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
There are no additional links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing