Drug information
MK-8591D (islatravir and lenacapavir fixed dose combination)
Not provided
Small molecule
Islatravir and Lenacapavir (ISL+LEN) is an investigational drug combination currently in clinical development for the treatment of HIV-1. Islatravir (MK-8591) is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor under evaluation in several ongoing clinical trials. Lenacapavir is a first in-class HIV-1 capsid inhibitor also being studied as a potential long-acting option in multiple ongoing studies for HIV treatment. The ISL+LEN combination is a proposed once-weekly oral fixed-dose combination regimen consisting of ISL 2mg and LEN 300mg. Once-weekly dosing has the potential to address adherence challenges versus daily oral ART. The pharmacokinetic profiles and potent antiviral activities of both ISL and LEN support their continued development as an investigational drug combination.
Islatravir and lenacapavir (ISL+LEN) is an investigational drug combination and is not currently approved in any jurisdiction globally. The safety and efficacy of the ISL+LEN combination has not yet been established. Pivotal studies are ongoing (Phase III ISLEND-1 and ISLEND-2 studies of lenacapavir/islatravir for the treatment of virally suppressed HIV)
In March 2021, Gilead Sciences and Merck announced that they have entered into an agreement to co-develop and co-commercialize long-acting treatments in HIV that combine Gilead’s investigational capsid inhibitor, lenacapavir, and Merck’s investigational nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor, islatravir, into a two-drug regimen with the potential to provide new treatment options for people living with HIV. Gilead Sciences anticipates a commercial launch of lenacapavir + islatravir for the treatment of HIV in 2027.
Therapeutic area(s)
- HIV
- Treatment
Administration route
Oral
Associated long-acting platforms
Oral solid form
Use of drug
- Self-administered
Not provided
Dosage
fixed dose combination of 300 mg lenacapavir + 2 mg islatravir
Not provided
Not provided
investigational doses used: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06630286
Not provided
Not provided
Formulations
Compare
Cabotegravir and Lenacapavir
Lenacapavir Once-Yearly
MK-8591D (Islatravir and Lenacapavir)
Teropavimab and Zinlirvimab
Associated technologies
Not provided
Comment & Information
Developer(s)

Merck & Co., Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical company known as Merck Sharp & Drone (MSD) in territories outside of the USA and Canada. Merck was originally established in 1891, and is headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey. The company is particularly well known for developing and manufacturing biologic therapies, vaccines, medicines and animal health products.

Gilead Sciences, Inc. is a multinational biopharmaceutical company that develops and manufactures innovative medicines for life-threatening diseases, including anti-viral therapeutics for HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and Covid-19. Headquartered in Foster City, California, Gilead was originally founded in 1987 and is currently listed on both the S&P 500 and the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index.
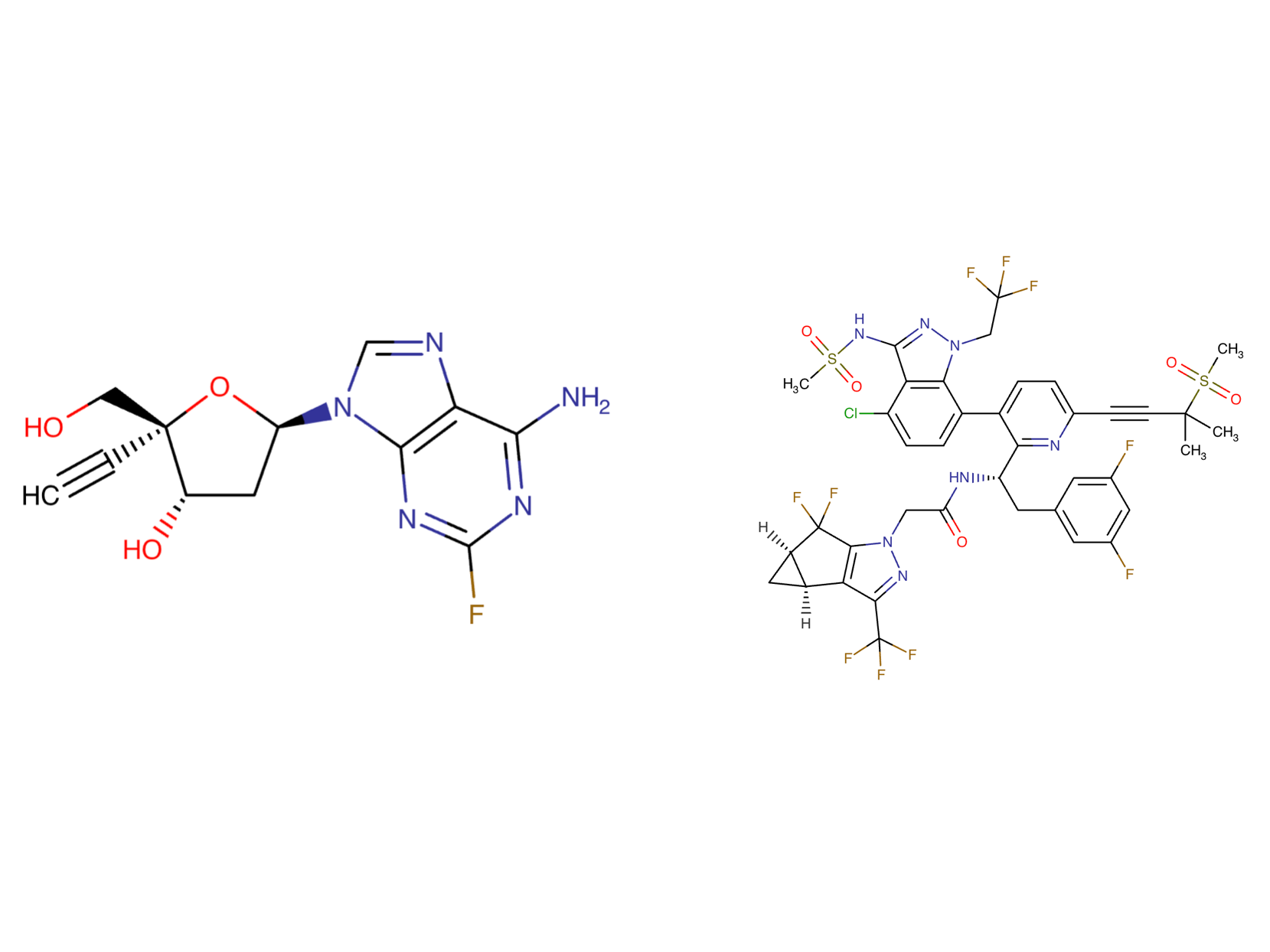
Drug structure
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
Lenacapavir is commercially manufactured by Gilead Sciences. Several synthetic chemical processes describing the manufacture of islatravir (ISL) have been published. However, these approaches have proved to be complex and highly inefficient, with marked difficulty in controlling 2’-deoxyribonucleoside anomer stereochemistry and the requirement for several protecting-group manipulations. To counter these issues, Merck developed a highly innovative and extraordinarily efficient approach utilising directed evolution to create a novel three-step biocatalytic cascade for ISL synthesis.
Islatravir: EasyMax 102 and 402 equipped with FireStringO2 sensors and the EasySampler 1210 system. A thermal gas flow controller (Aalborg, USA) to monitor and control oxidation air-gas flow to the reactor, with a suitable compressed air-source. Lenacapavir: Stainless steel pharmaceutical reactors, glass-lined reactors, rotary evaporator (rotovap), flash chromatography columns, stainless steel autoclave, cooling bath, silica gel chromatography columns, vacuum distillation apparatus, simulated moving bed chromatography system, Chiralpak columns.
For Islatravir synthesis, the automated lab reactor platforms EasyMax 102 and 402 (Mettler-Toledo AG, AutoChem, Switzerland) were utilised by Merck for reaction scale-up. Although ISL+LEN is currently being evaluated as a fixed-dose oral regimen, future studies may permit LEN to be administered via subcutaneous injection. In this instance, storage of injectable lenacapavir in borosilicate vials is contraindicated due to issues with chemical compatibility. Instead, it is recommended that vials are made from aluminosilicate glass.
Islatravir: 400 MHz Briker AVANCE III and 500MHz Bruker Ultrashield spectrometer (or equivalent) for 1H, 19F, 31P and 13C NMR. An Accurate-Mass Time-of-Flight (TOF) high resolution mass spectrometer. Molecular Devices plate reader Spectra Max Plus for Spectrophotomeric analyses, alongside a Perkin Elmer polarimeter with a PCB 1500 water Peltier system for optical rotation measurements. Lenacapavir: Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC).
Excipients
No proprietary excipient used
No novel excipient or existing excipient used
No residual solvent used
Delivery device(s)
No delivery device
There are either no relevant patents or these were not yet submitted to LAPaL
Publications
Amy E Colson, Gordon E Crofoot, Peter J Ruane, Moti N Ramgopal, Alexandra W Dretler, Ronald G Nahass, Gary I Sinclair, Mezgebe Berhe, Fadi Shihadeh, Shan-Yu Liu, Stephanie Klopfer, Sharline Madera, Hadas Dvory-Sobol, Martin Rhee, Elizabeth G Rhee, Jared Baeten, Joseph J Eron, 577. Week 48 Results of a Phase 2 Study Evaluating Once-weekly Oral Islatravir Plus Lenacapavir, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, Volume 12, Issue Supplement_1, February 2025, ofae631.015, https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofae631.015
Both islatravir (ISL), a nucleotide reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor, and lenacapavir (LEN), a capsid inhibitor, have potent anti-HIV-1 activity and pharmacokinetic profiles permitting once-weekly oral dosing. Week (W) 24 data (primary endpoint) from the current Phase 2 study were previously reported (CROI 2024); weekly oral ISL 2 mg + LEN 300 mg maintained high rates of viral suppression (HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL) with no clinically relevant decreases in CD4+ T-cells or lymphocytes, which had been previously observed with higher ISL doses. Here, we report W48 results.
In this Phase 2, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (NCT05052996), virologically suppressed adults on bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) were randomized 1:1 to receive weekly oral ISL 2 mg + LEN 300 mg or to continue daily B/F/TAF. Virologic outcomes (using FDA-defined snapshot algorithm), adverse events (AEs), CD4+ T-cells, and lymphocytes were assessed.
Additional documents
Useful links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing