Drug name
Islatravir (ISL)
Developer(s)
Drug information
Islatravir
Not provided
Small molecule
NRTTI
Islatravir (ISL), also known as MK-8591, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) in clinical development for HIV treatment. ISL is a first-in-class compound with a varied mechanism of action including a strong binding affinity for reverse transcriptase, the ability to block HIV primer translocation and an extended half-life enabling once-weekly oral dosing. ISL is being evaluated in several clinical trials in combination with other antiretroviral therapies including doravirine, lenacapavir and MK-8507. In 2021, the US FDA placed a clinical hold on ISL following a decrease in CD4 T-cell counts in HIV-positive patients, and reduced total lymphocyte counts in HIV-negative trial participants. The FDA clinical hold was lifted after Merck introduced lower ISL dosing
Unknown
Unknown
Therapeutic area(s)
- HIV
- Treatment
Administration route
Oral, Subcutaneous
Associated long-acting platforms
Polymeric implant, Oral solid form
Use of drug
- Administered by a nurse
- Administered by a specialty health worker
- Self-administered
Not provided
Not provided
Dosage
investigational
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Comment & Information
Developer(s)

Merck & Co., Inc.
Merck & Co., Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical company known as Merck Sharp & Drone (MSD) in territories outside of the USA and Canada. Merck was originally established in 1891, and is headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey. The company is particularly well known for developing and manufacturing biologic therapies, vaccines, medicines and animal health products.
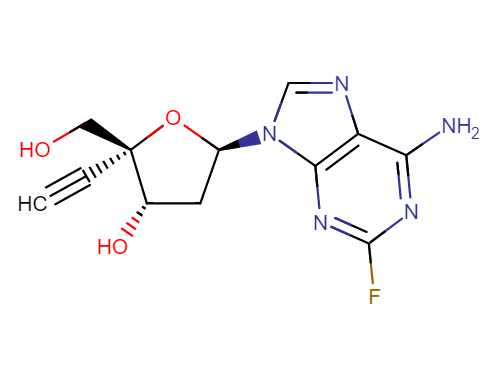
Drug structure
Scale-up and manufacturing prospects
The automated lab reactor platforms EasyMax 102 and 402 (Mettler-Toledo AG, AutoChem, Switzerland) were utilised by Merck for the reaction scale-up of Islatravir synthesis. The EasyMax reactors contained integrated measurement probes for pH and temperature, FireStringO2 dissolved oxygen sensors (Pyro-Science GmbH, Germany) and the EasySampler 1210 automated sampling system.
EasyMax 102 and 402 equipped with FireStringO2 sensors and the EasySampler 1210 system. A thermal gas flow controller (Aalborg, USA) to monitor and control oxidation air-gas flow to the reactor, with a suitable compressed air-source. Reactions at the 1L scale should be conducted using the Optimal 1001 automated lab reactor platform (Mettler-Toledo) or equivalent, alongside a sintered steel frit for improved 1L gas distribution for the oxidation reactions.
Several synthetic chemical processes describing the manufacture of ISL have been published, with each approach containing around twelve and eighteen steps. However, it should be noted that these approaches have proved to be complex and highly inefficient, with marked difficulty in controlling 2’-deoxyribonucleoside anomer stereochemistry and the requirement for several protecting-group manipulations. To counter these issues, Merck developed a highly innovative and extraordinarily efficient approach utilising directed evolution to create a novel three-step biocatalytic cascade for ISL synthesis
400 MHz Briker AVANCE III and 500MHz Bruker Ultrashield spectrometer (or equivalent) for 1H, 19F, 31P and 13C NMR. An Accurate-Mass Time-of-Flight (TOF) high resolution mass spectrometer. Molecular Devices plate reader Spectra Max Plus for Spectrophotomeric analyses, alongside a Perkin Elmer polarimeter with a PCB 1500 water Peltier system for optical rotation measurements. Aglient 7890A instrument for gas chromatography. UPLC via Agilent Technologies 1290 Infinity II series or HPLC through Agilent 1100 Series. Corona Ultra RS detector by Dionex for supercritical fluid chromatography.
Excipients
Not provided
Not provided
Not provided
Delivery device(s)
Not provided
Publications
Derbalah, Abdallaha,b; Karpick, Hayley Christineb,∗; Maize, Hollyb,∗; Skersick, Prestonb,∗; Cottrell, Mackenzieb; Rao, Gauri G.b. Role of islatravir in HIV treatment and prevention: an update. Current Opinion in HIV and AIDS: July 2022 - Volume 17 - Issue 4 - p 240-246
Purpose of review
To summarize recent updates on the potential role of islatravir for HIV treatment and prevention.
Recent findings
Islatravir is an investigational antiretroviral agent with unique pharmacologic properties that facilitate flexible dosing regimens. Islatravir has demonstrated potent antiviral activity and a high barrier to resistance when combined with doravirine and lamivudine. A simplified two-drug HIV treatment regimen of islatravir combined with doravirine has also demonstrated comparable efficacy to standard of care three-drug regimens. The long half-life and high potency of islatravir's active metabolite may support its use as a long-acting option for HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP). A once monthly oral dose of islatravir maintains effective concentrations of its active metabolite over the entire dosing interval. Furthermore, an investigational implantable formulation has been projected to provide efficacious concentrations for at least a year and exhibits comparable distribution into vaginal and rectal tissues making it a promising PrEP option for male and female individuals. Islatravir has minimal risks of drug interactions as it is not a substrate, inducer, or inhibitor of major drug metabolizers and transporters. Finally, clinical trials demonstrate islatravir's favorable safety profile revealing only mild and transient adverse events.
Summary
Leveraging the unique pharmacological properties of islatravir offers opportunities for simplified HIV treatment regimens and long-acting PrEP making it a valuable addition to the antiretroviral arsenal.
Beloor J, Kudalkar SN, Buzzelli G, Yang F, Mandl HK, Rajashekar JK, Spasov KA, Jorgensen WL, Saltzman WM, Anderson KS, Kumar P. Long-acting and extended-release implant and nanoformulations with a synergistic antiretroviral two-drug combination controls HIV-1 infection in a humanized mouse model. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021 Jun 26;7(1):e10237. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/btm2.10237. PMID: 35079625; PMCID: PMC8780078.
The HIV pandemic has affected over 38 million people worldwide with close to 26 million currently accessing antiretroviral therapy (ART). A major challenge in the long-term treatment of HIV-1 infection is nonadherence to ART. Long-acting antiretroviral (LA-ARV) formulations, that reduce dosing frequency to less than once a day, are an urgent need that could tackle the adherence issue. Here, we have developed two LA-ART interventions, one an injectable nanoformulation, and the other, a removable implant, for the delivery of a synergistic two-drug ARV combination comprising a pre-clinical nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), Compound I, and the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), 4′-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2′-deoxyadenosine. The nanoformulation is poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-based and the implant is a copolymer of ω-pentadecalactone and p-dioxanone, poly(PDL-co-DO), a novel class of biocompatible, biodegradable materials. Both the interventions, packaged independently with each ARV, released sustained levels of the drugs, maintaining plasma therapeutic indices for over a month, and suppressed viremia in HIV-1-infected humanized mice for up to 42 days with maintenance of CD4+ T cells. These data suggest promise in the use of these new drugs as LA-ART formulations in subdermal implant and injectable mode.
Huffman, M.A., Fryszkowska, A., Alvizo, O., Borra-Garske, M., Campos, K.R., Canada, K.A., Devine, P.N., Duan, D., Forstater, J.H., Grosser, S.T., Halsey, H.M., Hughes, G.J., Jo, J., Joyce, L.A., Kolev, J.N., Liang, J., Maloney, K.M., Mann, B.F., Marshall, N.M. and McLaughlin, M. (2019). Design of an in vitro biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of islatravir. Science, 366(6470), pp.1255–1259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay8484.
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions have begun to transform pharmaceutical manufacturing, offering levels of selectivity and tunability that can dramatically improve chemical synthesis. Combining enzymatic reactions into multistep biocatalytic cascades brings additional benefits. Cascades avoid the waste generated by purification of intermediates. They also allow reactions to be linked together to overcome an unfavorable equilibrium or avoid the accumulation of unstable or inhibitory intermediates. We report an in vitro biocatalytic cascade synthesis of the investigational HIV treatment islatravir. Five enzymes were engineered through directed evolution to act on non-natural substrates. These were combined with four auxiliary enzymes to construct islatravir from simple building blocks in a three-step biocatalytic cascade. The overall synthesis requires fewer than half the number of steps of the previously reported routes.
McLaughlin M, Kong J, Belyk KM, Chen B, Gibson AW, Keen SP, Lieberman DR, Milczek EM, Moore JC, Murray D, Peng F, Qi J, Reamer RA, Song ZJ, Tan L, Wang L, Williams MJ. Enantioselective Synthesis of 4'-Ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine (EFdA) via Enzymatic Desymmetrization. Org Lett. 2017 Feb 17;19(4):926-929. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00091. Epub 2017 Feb 6. PMID: 28165251.
An enantioselective synthesis of the potent anti-HIV nucleoside EFdA is presented. Key features of stereocontrol include construction of the fully substituted 4'-carbon via a biocatalytic desymmetrization of 2-hydroxy-2-((triisopropylsilyl)ethynyl)propane-1,3-diyl diacetate and a Noyori-type asymmetric transfer hydrogenation to control the stereochemistry of the 3'-hydroxyl bearing carbon. The discovery of a selective crystallization of an N-silyl nucleoside intermediate enabled isolation of the desired β-anomer from the glycosylation step.
Kageyama M, Nagasawa T, Yoshida M, Ohrui H, Kuwahara S. Enantioselective total synthesis of the potent anti-HIV nucleoside EFdA. Org Lett. 2011 Oct 7;13(19):5264-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ol202116k. Epub 2011 Sep 2. PMID: 21888325.
A concise enantioselective total synthesis of 4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine (EFdA), an extremely potent anti-HIV agent, has been accomplished from (R)-glyceraldehyde acetonide in 18% overall yield by a 12-step sequence involving a highly diastereoselective ethynylation of an α-alkoxy ketone intermediate.
Fukuyama K, Ohrui H, Kuwahara S. Synthesis of EFdA via a diastereoselective aldol reaction of a protected 3-keto furanose. Org Lett. 2015 Feb 20;17(4):828-31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ol5036535. Epub 2015 Feb 2. PMID: 25642994.
An efficient enantioselective total synthesis of EFdA, a remarkably potent anti-HIV nucleoside analogue with various favorable pharmacological profiles, has been achieved in 37% overall yield from diacetone-D-glucose by a 14-step sequence that features a highly diastereoselective installation of the tetrasubstituted stereogenic center at the C4' position, direct oxidative cleavage of an acetonide-protected diol derivative to an aldehyde, and one-pot 2'-deoxygenation of a ribonucleoside intermediate.
Kageyama M, Miyagi T, Yoshida M, Nagasawa T, Ohrui H, Kuwahara S. Concise synthesis of the anti-HIV nucleoside EFdA. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(6):1219-25. doi: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.120134. Epub 2012 Jun 7. PMID: 22790950.
EFdA (4'-ethynyl-2-fluoro-2'-deoxyadenosine), a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with extremely potent anti-HIV activity, was concisely synthesized from (R)-glyceraldehyde acetonide in an 18% overall yield by a 12-step sequence involving highly diastereoselective ethynylation of an α-alkoxy ketone intermediate. The present synthesis is superior, both in overall yield and in the number of steps, to the previous one which required 18 steps from an expensive starting material and resulted in a modest overall yield of 2.5%.
Kinvig, H., Cottura, N., Lloyd, A. et al. Evaluating Islatravir Administered Via Microneedle Array Patch for Long-Acting HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 47, 855–868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-022-00793-6
Technologies for long-acting administration of antiretrovirals (ARVs) for the prevention and treatment of HIV are at the forefront of research initiatives aiming to tackle issues surrounding drug adherence with the current standard of once-daily oral administration. Islatravir (ISL) is an emerging ARV that shows promising characteristics for long-acting prevention and treatment both orally as well as through alternative routes of administration. Microneedle array patches (MAPs) are a pain-free and discreet transdermal delivery technology that offer extended-release administration of nanoparticulate drugs. This study aimed to utilise physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling to predict the pharmacokinetics resulting from ISL administered via MAP and to identify key MAP characteristics required to sustain effective concentrations over extended dosing intervals.
Additional documents
No documents were uploaded
Useful links
Collaborate for development
Consider on a case by case basis, collaborating on developing long acting products with potential significant public health impact, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), utilising the referred to long-acting technology
Share technical information for match-making assessment
Provide necessary technical information to a potential partner, under confidentiality agreement, to enable preliminary assessment of whether specific medicines of public health importance in LMICs might be compatible with the referred to long-acting technology to achieve a public health benefit
Work with MPP to expand access in LMICs
In the event that a product using the referred to long-acting technology is successfully developed, the technology IP holder(s) will work with the Medicines Patent Pool towards putting in place the most appropriate strategy for timely and affordable access in low and middle-income countries, including through licensing